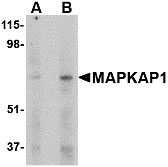
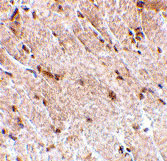
MAPKAP1 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9BPZ7 |
| Other Accession | NP_001006618, 56788407 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 59123 Da |
| Application Notes | MAPKAP1 antibody can be used for detection of MAPKAP1 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 79109 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | MAPKAP1 Antibody: MIP1, SIN1, JC310, SIN1b, SIN1g, MIP1, Target of rapamycin complex 2 subunit MAPKAP1, Mitogen-activated protein kinase 2-associated protein 1, TORC2 subunit MAPKAP1, mitogen-activated protein kinase associated protein 1 |
| Target/Specificity | MAPKAP1; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | MAPKAP1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | MAPKAP1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | MAPKAP1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:15363842, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:18752} |
|---|---|
| Function | Component of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2), which transduces signals from growth factors to pathways involved in proliferation, cytoskeletal organization, lipogenesis and anabolic output (PubMed:15467718, PubMed:16919458, PubMed:16962653, PubMed:17043309, PubMed:21806543, PubMed:28264193, PubMed:28968999, PubMed:30837283, PubMed:35926713). In response to growth factors, mTORC2 phosphorylates and activates AGC protein kinase family members, including AKT (AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3), PKC (PRKCA, PRKCB and PRKCE) and SGK1 (PubMed:16919458, PubMed:16962653, PubMed:21806543, PubMed:28264193, PubMed:28968999, PubMed:30837283, PubMed:35926713). In contrast to mTORC1, mTORC2 is nutrient-insensitive (PubMed:16962653). Within the mTORC2 complex, MAPKAP1/SIN1 acts as a substrate adapter which recognizes and binds AGC protein kinase family members for phosphorylation by MTOR (PubMed:21806543, PubMed:28264193). mTORC2 plays a critical role in AKT1 activation by mediating phosphorylation of different sites depending on the context, such as 'Thr-450', 'Ser- 473', 'Ser-477' or 'Thr-479', facilitating the phosphorylation of the activation loop of AKT1 on 'Thr-308' by PDPK1/PDK1 which is a prerequisite for full activation (PubMed:28264193, PubMed:35926713). mTORC2 catalyzes the phosphorylation of SGK1 at 'Ser-422' and of PRKCA on 'Ser-657' (PubMed:30837283, PubMed:35926713). The mTORC2 complex also phosphorylates various proteins involved in insulin signaling, such as FBXW8 and IGF2BP1 (By similarity). mTORC2 acts upstream of Rho GTPases to regulate the actin cytoskeleton, probably by activating one or more Rho-type guanine nucleotide exchange factors (PubMed:15467718). mTORC2 promotes the serum-induced formation of stress-fibers or F-actin (PubMed:15467718). MAPKAP1 inhibits MAP3K2 by preventing its dimerization and autophosphorylation (PubMed:15988011). Inhibits HRAS and KRAS independently of mTORC2 complex (PubMed:17303383, PubMed:34380736, PubMed:35522713). Enhances osmotic stress-induced phosphorylation of ATF2 and ATF2-mediated transcription (PubMed:17054722). Involved in ciliogenesis, regulates cilia length through its interaction with CCDC28B independently of mTORC2 complex (PubMed:23727834). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Early endosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Late endosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Lysosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Golgi apparatus membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Mitochondrion outer membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. Nucleus Note=The mTORC2 complex localizes to membranes: mTORC2 is active at the plasma membrane, endoplasmic reticulum membrane, lysosomes and perinuclear region (PubMed:17303383, PubMed:21867682, PubMed:30837283) Iin lysosomal membrane, mTORC2 is sensitive to lysosomal positioning in the cell (PubMed:31130364). Following phosphorylation by PKC, localizes to the perinuclear region, where the mTORC2 complexe specifically phosphorylates SGK1, but not AKT (PubMed:30837283) [Isoform 2]: Cell membrane. Nucleus [Isoform 6]: Cytoplasm. Nucleus |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitously expressed, with highest levels in heart and skeletal muscle. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
MAPKAP1 Antibody: MAPKAP1 was initially identified as the human homolog of S. pombe SIN1. Recent evidence has shown that it identical to Mip1, a protein that interacts with MEKK2, a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) intracellular signaling network. MAPKAP1 is thought to prevent MEKK2 activation and dimerization by forming a complex with the inactive and non-phosphorylated MEKK2, thereby blocking the JNK1/2, ERK1/2, p38 and ERK5 MAPKs. MAPKAP1 has also been shown to play a role in the TOR signaling process, a pathway that is involved in controlling cell growth and proliferation in response to environmental cues such as nutrients, growth factors and hormones. Experiments showed that MAPKAP1 helped to maintain the TOR/rictor assembly but not the TOR/RAPTOR complex, which allowed specific phosphorylation of Akt, a kinase that is believed to couple the growth factor-PI3K signaling pathway to the nutrient-regulated TOR signaling pathway. Multiple alternatively spliced isoforms of MAPKAP1 have been identified.
References
Schroder W, Cloonan N, Bushell G, et al. Alternative polyadenylation and splicing of mRNAs transcribed from the human Sin1 gene. Gene2004; 339:17-23.
Cheng J, Zhang D, Kim K, et al. Mip1, an MEKK2-interacting protein, controls MEKK2 dimerization and activation. Mol. Cell. Biol.2005; 25:5955-64.
Jacinto E, Facchinetti V, Liu D, et al. SIN1/MIP1 maintains rictor-mTOR complex integrity and regulates Akt phosphorylation and substrate specificity. Cell2006; 127:125-37.
Wullschleger S, Loewith R and Hall MN. TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell2006; 124:471-84.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.