IA-1 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q01101 |
| Other Accession | NP_002187, 4504713 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 52923 Da |
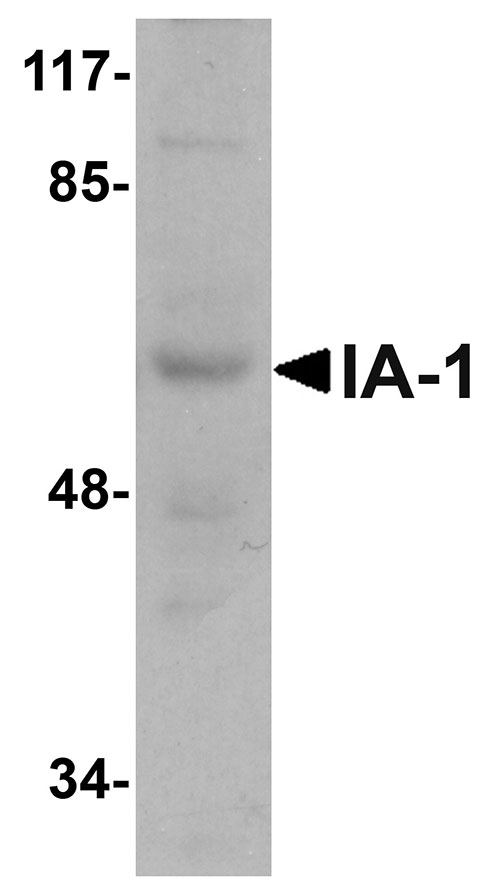
| Application Notes | IA-1 antibody can be used for detection of IA-1 by Western blot at 1 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 3642 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | INSM1; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | IA-1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | IA-1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | INSM1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | IA1 |
| Function | Sequence-specific DNA-binding transcriptional regulator that plays a key role in neurogenesis and neuroendocrine cell differentiation during embryonic and/or fetal development. Binds to the consensus sequence 5'-[TG][TC][TC][TT][GA]GGG[CG]A-3' in target promoters. Acts as a transcriptional repressor of NEUROD1 and INS expression via its interaction with cyclin CCND1 in a cell cycle- independent manner. Negatively regulates skeletal muscle-specific gene expression in endocrine cells of the pituitary by inhibiting the Notch signaling pathway. Represses target gene transcription by recruiting chromatin-modifying factors, such as HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, KDM1A and RCOR1 histone deacetylases. Binds to its own promoter, suggesting autoregulation as a self-control feedback mechanism. Competes with histone H3 for the same binding site on the histone demethylase complex formed by KDM1A and RCOR1, and thereby inhibits demethylation of histone H3 at 'Lys-4' (PubMed:23721412). Promotes the generation and expansion of neuronal basal progenitor cells in the developing neocortex. Involved in the differentiation of endocrine cells of the developing anterior pituitary gland, of the pancreas and intestine, and of sympatho-adrenal cells in the peripheral nervous system. Promotes cell cycle signaling arrest and inhibition of cellular proliferation. |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63ZV0}. |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in pancreatic duct cells. Expressed in several tumor cell lines of neuroendocrine origin including pheochromocytoma, medullary thyroid carcinoma, insulinoma, medulloblastoma, retinoblastoma, pheochromacytoma, medullary thyroid carcinoma and small cell lung carcinoma. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
IA-1 Antibody: IA-1, also known as INSM1, is an essential five zinc-finger transcription factor that while initially identified from an insulinoma cDNA library, is expressed in the developing nervous system. Specifically, IA-1 is expressed as early as E9.5 in mice in the fore-, mid- and hindbrain, spinal cord, retina, and olfactory bulb. It is thought that IA-1 functions as a transcriptional repressor, and is a part of several signaling pathways including those of Notch and sonic hedgehog in addition to that of Ngn3 during pancreatic endocrine cell differentiation. IA-1 is also expressed in multiple tumors, including the majority of neuroendocrine tumors tested so far as well as nearly 100% of all small cell lung carcinomas, indicating that IA-1 may be an important target in cancer therapy.
References
Lan MS, Li Q, Lu J, et al. Genomic organization, 5’-upstream sequence, and chromosomal localization of an insulinoma-associated intronless gene, IA-1. J. Biol. Chem.1994; 269:14170-4.
Jacob J, Storm R, Castro DS, et al. Insm (IA-1) is an essential component of the regulatory network that specifies monoaminergic neuronal phenotypes in the vertebrate hindbrain. Dev.2009; 136:2477-85.
Breslin MB, Zhu M, and Lan MS. NeuroD1/E47 regulates the E-box element of a novel zinc-finger transcription factor, IA-1, in developing nervous system. J. Biol. Chem.2003; 278:38991-7.
Nelson BR, Hartman BH, Georgi SA, et al. Transient inactivation of Notch signaling synchronizes differentiation of neural progenitor cells. Dev. Biol.2007; 304:479-98.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.