SRPX1 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P78539 |
| Other Accession | NP_006298, 5454086 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 51572 Da |
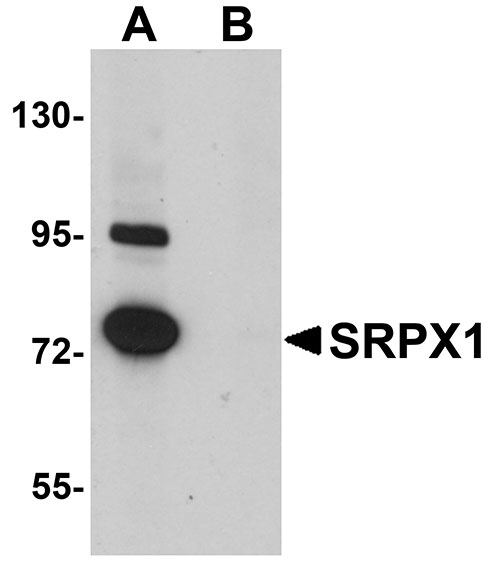
| Application Notes | SRPX1 antibody can be used for detection of SRPX1 by Western blot at 0.25 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 8406 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | SRPX; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | SRPX1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | SRPX1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | SRPX |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | ETX1 |
| Function | May be involved in phagocytosis during disk shedding, cell adhesion to cells other than the pigment epithelium or signal transduction. |
| Cellular Location | Cell surface. Note=Possibly surface of photoreceptor cell |
| Tissue Location | Detected in fibroblasts (at protein level) (PubMed:36213313). Retina and heart; less in placenta, pancreas, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney and brain |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
SRPX1 Antibody: SRPX1 was initially identified as a candidate gene for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa and is overexpressed in the trabecular network of the eye in glaucoma conditions. Its expression is significantly downregulated in a number cancer cell lines and malignant tumor tissues and its ectopic expression induces apoptosis through the endoplasmic reticulum and the activation of caspase-12, -9, and -3, indicating that it can function as a tumor suppressor. SRPX1 is also involved with the regulation of autophagy under low serum conditions and can associate with Rab24, a member of the Rab GTPase protein family that is involved in autophagy. This association of SRPX1 with Rab24 is enhanced during autophagy.
References
Dry KL, Aldred MA, Edgar AJ, et al. Identification of a novel gene, ETX1 from Xp21.1, a candidate gene for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (RP3). Hum. Mol. Genet.1995; 4:2347-53.
Iragavarapu S, Algeciras ME, Lee RK, et al. ETX1 is over-expressed in the glaucomatous trabecular meshwork. Mol. Vision2009; 15:2061-7.
Shimakage M, Kawahara K, Kikkawa N, et al. Downregulation of drs mRNA in human colon adenocarcinomas. Int. J. Cancer2000; 87:5-11.
Tambe Y, Isono T, Haraguchi S, et al. A novel apoptotic pathway induced by the drs tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene2004; 23:2977-87.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.