KPNA4 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

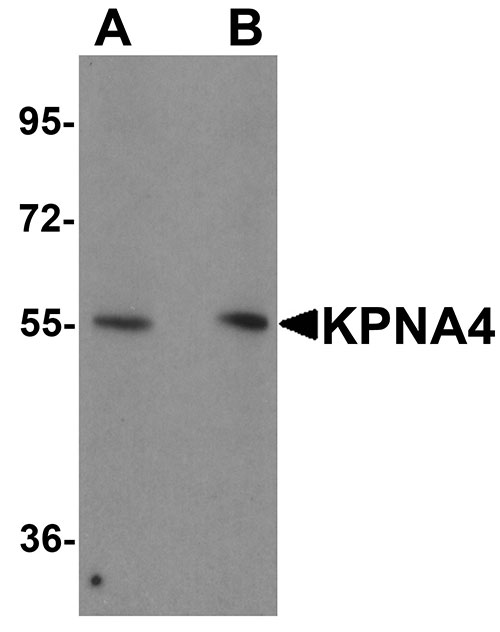
Application
| WB, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O00629 |
| Other Accession | EAW78632, 119599038 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 57887 Da |
| Application Notes | KPNA4 antibody can be used for detection of KPNA4 by Western blot at 1 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunocytochemistry starting at 2.5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 3840 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | KPNA4; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | KPNA4 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | KPNA4 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | KPNA4 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:38512451, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:6397} |
|---|---|
| Function | Functions in nuclear protein import as an adapter protein for nuclear receptor KPNB1 (PubMed:10567565, PubMed:20818336, PubMed:28760339, PubMed:29042532, PubMed:38512451). Binds specifically and directly to substrates containing either a simple or bipartite NLS motif (PubMed:20818336, PubMed:28760339, PubMed:29042532, PubMed:38512451). Docking of the importin/substrate complex to the nuclear pore complex (NPC) is mediated by KPNB1 through binding to nucleoporin FxFG repeats and the complex is subsequently translocated through the pore by an energy requiring, Ran-dependent mechanism (PubMed:20818336, PubMed:28760339, PubMed:29042532, PubMed:38512451). At the nucleoplasmic side of the NPC, Ran binds to importin-beta and the three components separate and importin-alpha and -beta are re- exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where GTP hydrolysis releases Ran from importin (PubMed:20818336, PubMed:28760339, PubMed:29042532, PubMed:38512451). The directionality of nuclear import is thought to be conferred by an asymmetric distribution of the GTP- and GDP-bound forms of Ran between the cytoplasm and nucleus (PubMed:20818336, PubMed:28760339, PubMed:29042532, PubMed:38512451). Mediates nuclear import of AARS1, MRTFA and RANBP3 (PubMed:10567565, PubMed:20818336, PubMed:28760339, PubMed:38512451). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in testis, ovary, small intestine, heart, skeletal muscle, lung and pancreas, but barely detectable in kidney, thymus, colon and peripheral blood leukocytes |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
KPNA4 Antibody: Karyopherin, a cytosolic and heterodimeric protein complex consisting of alpha and beta subunits, is responsible for targeting proteins with nuclear localization signals to the nuclear pore complex by an energy requiring, Ran-dependent mechanism. The alpha subunit and imported substrate enter the nucleus and accumulate in the nucleoplasm, while the beta subunit accumulates at the NPC. Molecules containing the classical nuclear localization signal (NLS) are transported into the nucleus by alpha/beta heterodimers. KPNA3 has been shown to be important in the TNF-α-induced nuclear import of NF-κB. It is also involved in the stress-mediated nuclear stabilization of p53 and the nuclear import and replication of HIV-1 in both dividing and non-dividing cells.
References
Moroianu J. Molecular mechanisms of nuclear protein transport. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr.1997; 7:61-72.
Gilchrist D and Rexach M. Molecular basis for the rapid dissociation of nuclear localization signals from karyopherin alpha in the nucleoplasm. J. Biol. Chem.2003; 278: 51937-49.
Goldfarb DS, Corbett AH, Mason DA, et al. Importin alpha: a multi-purpose nuclear-transport receptor. Trends Cell Biol.2004; 14:505-14.
Fagerlund R, Melen K, Cao X, et al. NF-kappaB p52, RelB, and c-Rel are transported into the nucleus via a subset of importin alpha molecules. Cell Signal.2008; 20:1442-51.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.