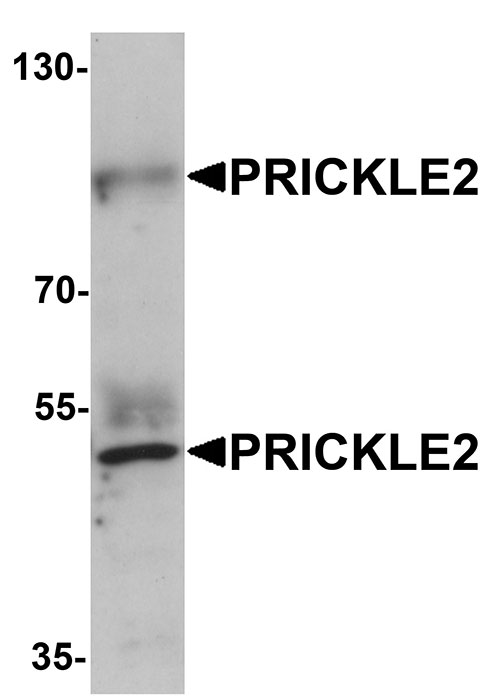
PRICKLE2 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q7Z3G6 |
| Other Accession | NP_942559, 38524620 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 95615 Da |
| Application Notes | PRICKLE2 antibody can be used for detection of PRICKLE2 by Western blot at 1 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunofluorescence starting at 20 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 166336 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | PRICKLE2; Two isoforms of PRICKLE2 are known to exist. PRICKLE2 antibody is predicted to not cross-react with other PRICKLE protein family members. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | PRICKLE2 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | PRICKLE2 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | PRICKLE2 |
|---|---|
| Cellular Location | Nucleus membrane. |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in brain, eye and testis. Additionally in fetal brain, adult cartilage, pancreatic islet, gastric cancer and uterus tumors. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
PRICKLE2 Antibody: PRICKLE2, also known as Pk2 or EPM5, is a member of a highly conserved protein family that function in the noncanonical WNT signaling pathway which regulates intracellular calcium release and planar cell polarity. Both PRICKLE2 and the related protein PRICKLE1 are expressed in postmitotic neurons and promote neurite outgrowth, and both proteins promote neurite outgrowth via the Dishevelled dependent pathway in C1300 cells. PRICKLE2 localizes to the postsynaptic density and interacts with PSD-95 and NMDA receptors. Defects in the gene encoding PRICKLE2 are associated with autosomal recessive progressive myoclonic epilepsy.
References
Katoh M and Katoh M. Identification and characterization of human PRICKLE1 and PRICKLE2 genes as well as mouse Prickle1 and Prickle2 genes homologous to Drosophila tissue polarity gene prickle. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2003; 11:249-56.
Veeman MT, Slusarski DC, Kaykas A, et al. Zebrafish prickle, a modulator of noncanonical Wnt/Fz signaling, regulates gastrulation movements. Curr. Biol. 2003; 13:680-5.
Okuda H, Miyata S, Mori Y, et al. Mouse Prickle1 and Prickle2 are expressed in postmitotic neurons and promote neurite outgrowth. FEBS Lett. 2007; 581:4754-60
Fujimura L, Watanabe-Takano H, Sato Y, et al. Prickle promotes neurite outgrowth via the Dishevelled dependent pathway in C1300 cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2009; 467:6-10.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.