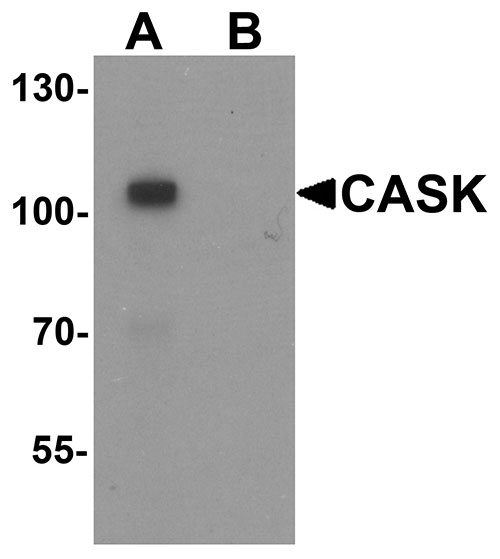
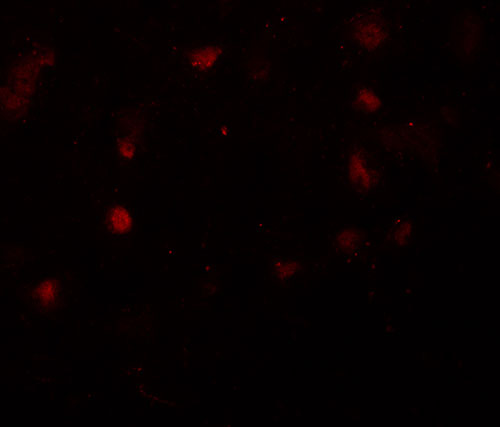
CASK Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O14936 |
| Other Accession | NP_003679, 186972120 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 105123 Da |
| Application Notes | CASK antibody can be used for detection of CASK by Western blot at 1 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 8573 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | CASK; At least six alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | CASK antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | CASK Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CASK (HGNC:1497) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | LIN2 |
| Function | Multidomain scaffolding Mg(2+)-independent protein kinase that catalyzes the phosphotransfer from ATP to proteins such as NRXN1, and plays a role in synaptic transmembrane protein anchoring and ion channel trafficking (PubMed:18423203). Contributes to neural development and regulation of gene expression via interaction with the transcription factor TBR1. Binds to cell-surface proteins, including amyloid precursor protein, neurexins and syndecans. May mediate a link between the extracellular matrix and the actin cytoskeleton via its interaction with syndecan and with the actin/spectrin-binding protein 4.1. Component of the LIN-10-LIN-2-LIN-7 complex, which associates with the motor protein KIF17 to transport vesicles containing N-methyl-D- aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit NR2B along microtubules (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62915}. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62915}. Cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62915}; Peripheral membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62915} |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitous. Expression is significantly greater in brain relative to kidney, lung, and liver and in fetal brain and kidney relative to lung and liver. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
CASK Antibody: CASK (Calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase), a conserved multi-domain scaffolding protein, belongs to a MAGUK (membrane-associated guanylate kinase homologs) subfamily and is involved in cell junction organization, tumor suppression and signaling. It is characterized by a novel domain structure that consists of a calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase domain followed by PDZ, SH3 and guanylate kinase-like (GUK) domains. CASK is ubiquitously expressed and significantly greater in brain where it is thought to be involved in signaling at neuronal synapses. CASK interacts with CASKINs and defects in CASK are the cause of mental retardation X-linked CASK-related.
References
Dimitratos SD, Woods DF, and Bryant PJ. Camguk, Lin-2, and CASK: novel membrane associated guanylate kinase homologs that also contain CaM kinase domains. Mech. Dev. 1997; 63:127-30.
Hsueh YP and Sheng M. Regulated expression and subcellular localization of syndecan heparan sulfate proteoglycans and the syndecan-binding protein CASK/LIN-2 during rat brain development. J. Neurosci. 1999;19:7415-25.
Tabuchi K, Biederer T, Butz S, et al. CASK participates in alternative tripartite complexes in which Mint 1 competes for binding with CASKIN2, a novel CASK-binding protein. J. Neurosci. 2002; 22:4264-73.
Kuo TY, Hong CJ, Chien HL, et al. X-linked mental retardation gene CASK interacts with Bcl11A/CTIP1 and regulates axon branching and outgrowth. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010; 88: 2364-73.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.