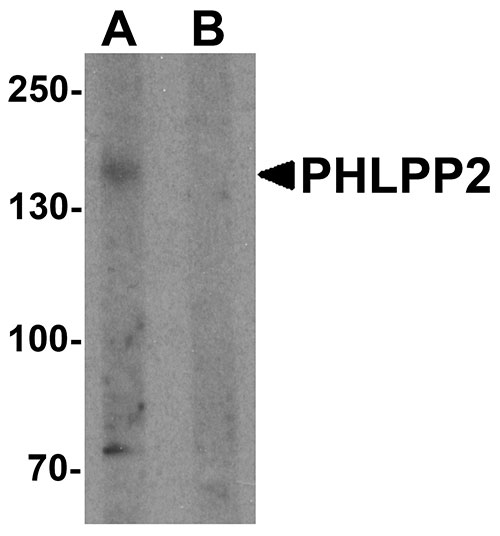
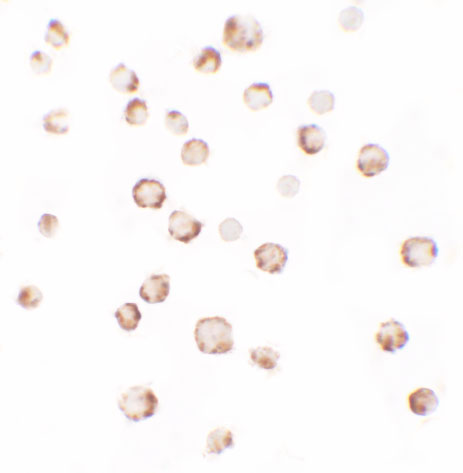
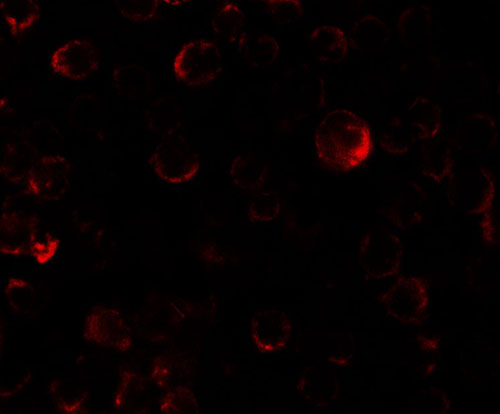
PHLPP2 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q6ZVD8 |
| Other Accession | NP_055835, 65301141 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 156 kDa |
| Application Notes | PHLPP2 antibody can be used for detection of PHLPP2 by Western blot at 1 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 23035 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | PHLPP2; At least three isoforms are known to exist; this antibody will detect the two largest isoforms. PHLPP2 antibody is predicted to not cross react with PHLPP1. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | PHLPP2 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | PHLPP2 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | PHLPP2 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | KIAA0931, PHLPPL |
| Function | Protein phosphatase involved in regulation of Akt and PKC signaling. Mediates dephosphorylation in the C-terminal domain hydrophobic motif of members of the AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family; specifically acts on 'Ser-473' of AKT1, 'Ser-660' of PRKCB isoform beta-II and 'Ser-657' of PRKCA. Akt regulates the balance between cell survival and apoptosis through a cascade that primarily alters the function of transcription factors that regulate pro- and antiapoptotic genes. Dephosphorylation of 'Ser-473' of Akt triggers apoptosis and decreases cell proliferation. Also controls the phosphorylation of AKT3. Dephosphorylates STK4 on 'Thr-387' leading to STK4 activation and apoptosis (PubMed:20513427). Dephosphorylates RPS6KB1 and is involved in regulation of cap-dependent translation (PubMed:21986499). Inhibits cancer cell proliferation and may act as a tumor suppressor. Dephosphorylation of PRKCA and PRKCB leads to their destabilization and degradation. Dephosphorylates RAF1 inhibiting its kinase activity (PubMed:24530606). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Nucleus. Note=In colorectal cancer tissue, expression is concentrated in the cytoplasm and nucleus |
| Tissue Location | In colorectal cancer tissue, expression is highest in the surface epithelium of normal colonic mucosa adjacent to the cancer tissue but is largely excluded from the crypt bases. Expression is lost or significantly decreased in 80% of tested tumors (at protein level). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
PHLPP2 Antibody: PHLPP2 is a member of the serine/threonine phosphatase family, which are important regulators of Akt serine-threonine kinases (AKT1, AKT2, AKT3) and conventional/novel protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms. PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 have a similar domain structure and have been shown to dephosphorylate and inactivate, distinct Akt isoforms, at one of the two critical phosphorylation sites required for activation: Serine473. PHLPP2 dephosphorylates AKT1 and AKT3, whereas PHLPP1 is specific for AKT2 and AKT3. PHLPP1 promotes apoptosis and may act as a tumor suppressor. PHLPP2 associates with and is inhibited by adenylyl cyclase type 6 (AC6), thereby allowing Akt activation.
References
Brognard J and Newton AC. PHLiPPing the switch on Akt and protein kinase C signaling. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2008; 19:223-30.
Gao T, Furnari F and Newton AC. PHLPP: a phosphatase that directly dephosphorylates Akt, promotes apoptosis, and suppresses tumor growth. Mol. Cell 2005; 18:13-24.
Brognard J, Sierecki E, Gao T, et al. PHLPP and a second isoform, PHLPP2, differentially attenuate the amplitude of Akt signaling by regulating distinct Akt isoforms. Mol. Cell 2007; 25:917-31
Gao MH, Miyanohara A, Feramisco JR, et al. Activation of PH-domain leucine-rich protein phosphatase 2 (PHLPP2) by agonist stimulation in cardiac myocytes expressing adenylyl cyclase type 6. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009; 384:193-8.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.