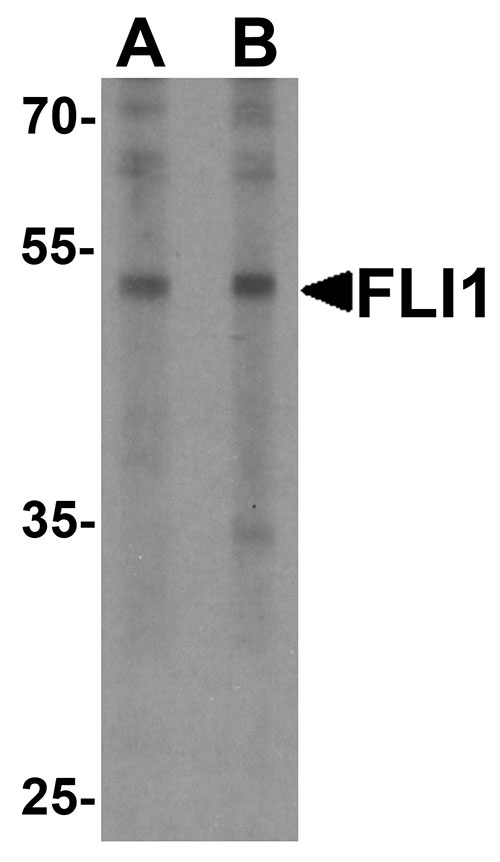
FLI1 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P20930 |
| Other Accession | NP_002008, 7110593 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | Predicted: 50 kDa Observed: 52kDa |
| Application Notes | FLI1 antibody can be used for detection of FLI1 by Western blot at 0.5 - 1 µg/ml. |
| Gene ID | 2312 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | FLI1; FLI1 antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive. At least four isoforms of FLI1 are known to exist; this antibody will detect all four. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | FLI1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | FLI1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | FLG |
|---|---|
| Function | Aggregates keratin intermediate filaments and promotes disulfide-bond formation among the intermediate filaments during terminal differentiation of mammalian epidermis. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasmic granule. Note=In the stratum granulosum of the epidermis, localized within keratohyalin granules (PubMed:1429717). In granular keratinocytes and in lower corneocytes, colocalizes with calpain-1/CAPN1 (PubMed:21531719). |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in skin, thymus, stomach, tonsils, testis, placenta, kidney, pancreas, mammary gland, bladder, thyroid, salivary gland and trachea, but not detected in heart, brain, liver, lung, bone marrow, small intestine, spleen, prostate, colon, or adrenal gland (PubMed:19384417). In the skin, mainly expressed in stratum granulosum of the epidermis (PubMed:1429717, PubMed:19384417) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The Friend leukemia virus integration 1 (FLI1) protein is a transcription factor containing an ETS DNA-binding domain and is highly expressed in hematopoietic cell lineages and vascular endothelial cells (1). FLI1 plays important roles in megakaryocytic differentiation (2) and vascular homeostasis (3). The FLI1 gene can undergo a t(11;22)(q24;q12) translocation with the Ewing sarcoma gene on chromosome 22, which results in a fusion gene that is present in the majority of Ewing sarcoma cases. (4). Abnormal expression of FLI1 can be used as an adverse prognostic indicator for acute myeloid leukemia (5).
References
Hollenhorst PC, Jones DA, and Graves BJ. Expression profiles frame the promoter specificity dilemma of the ETS family of transcription factors. Nuc. Acids Res. 2004; 32:5693-702.
Spyropoulos DD, Pharr PN, Lavenburg KR, et al. Hemorrhage, impaired hematopoiesis, and lethality in mouse embryos carrying a targeted disruption of the Fli1 transcription factor. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000; 20:5643-52.
Asano Y, Stawski L, Hant F, et al. Endothelial Fli1 deficiency impairs vascular homeostasis: a role in scleroderma vasculopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2010; 176:1983-98.
May WA, Gishizky ML, Lessnick SL, et al. Ewing sarcoma 11;22 translocation produces a chimeric transcription factor that requires the DNA-binding domain encoded by FLI1 for transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993; 90:5752-6.
5. Kornblau SM, Qiu YH, Zhang N, et al. Abnormal expression of FLI1 protein is an adverse prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2011; 118:5604-12.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.