IL-36A Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UHA7 |
| Other Accession | NP_055255, 7657092 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
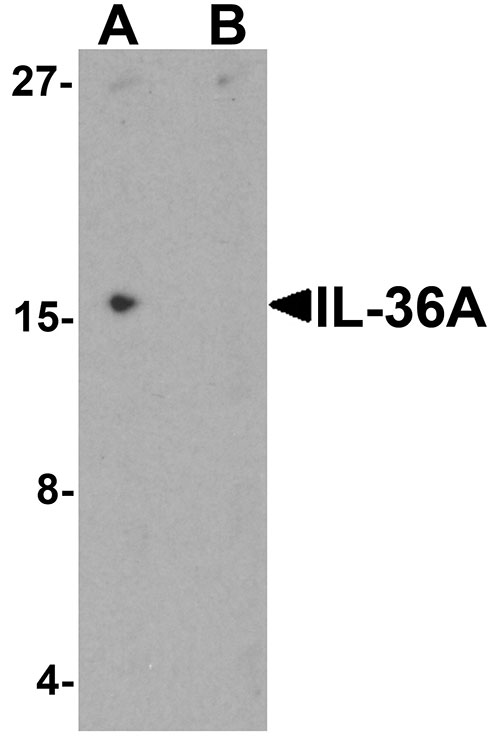
| Calculated MW | Predicted: 17 kDa Observed: 16 kDa |
| Application Notes | IL-36A antibody can be used for detection of IL-36A by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml. |
| Gene ID | 27179 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | IL36A; IL-36A antibody is human specific. IL-36A antibody will not cross-react with IL-36B or IL-36G. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | IL-36A antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | IL-36A Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | IL36A (HGNC:15562) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | FIL1E, IL1E, IL1F6 |
| Function | Cytokine that binds to and signals through the IL1RL2/IL-36R receptor which in turn activates NF-kappa-B and MAPK signaling pathways in target cells linked to a pro-inflammatory response. Part of the IL- 36 signaling system that is thought to be present in epithelial barriers and to take part in local inflammatory response; similar to the IL-1 system with which it shares the coreceptor IL1RAP. Seems to be involved in skin inflammatory response by acting on keratinocytes, dendritic cells and indirectly on T-cells to drive tissue infiltration, cell maturation and cell proliferation. In cultured keratinocytes induces the expression of macrophage, T-cell, and neutrophil chemokines, such as CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, CCL2, CCL17, CCL22, CL20, CCL5, CCL2, CCL17, CCL22, CXCL8, CCL20 and CXCL1, and the production of pro- inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha, IL-8 and IL-6. In cultured monocytes up-regulates expression of IL-1A, IL-1B and IL-6. In myeloid dendritic cells involved in cell maturation by up-regulating surface expression of CD83, CD86 and HLA-DR. In monocyte-derived dendritic cells facilitates dendritic cell maturation and drives T-cell proliferation. May play a role in pro-inflammatory effects in the lung. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Secreted. Note=The secretion is dependent on protein unfolding and facilitated by the cargo receptor TMED10; it results in protein translocation from the cytoplasm into the ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment) followed by vesicle entry and secretion. |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in immune system and fetal brain, but not in other tissues tested or in multiple hematopoietic cell lines Predominantly expressed in skin keratinocytes but not in fibroblasts, endothelial cells or melanocytes. Increased in lesional psoriasis skin |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
IL-36A is is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family whose gene and eight other interleukin 1 family genes form a cytokine gene cluster on chromosome 2 (1). IL-36A is thought to activate the NF-kappaB pathway through IL-1 receptor family members IL-1RL2 and IL-1RAcP (2). Like the related proteins IL-36B and IL-36G, IL-36A requires post-translational processing for full agonist activity, but the cleavage mechanism is currently unknown (3). The IL-36 cytokines have been suggested to amplify Th1 responses by enhancing proliferation and Th1 polarization of naive CD4+ T cells (4).
References
Smith DE, Renshaw BR, Ketchem RR, et al. Four new members expand the interleukin-1 superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 2000; 275:1169-75.
Towne JE, Garka KE, Renshaw BR, et al. Interleukin (IL)-1F6, IL-1F8, and IL-1F9 signal through IL-1Rrp2 and IL-1RAcP to activate the pathway leading to NF-kappaB and MAPKs. J. Biol. Chem. 2004; 279:13677-88.
Towne JE, Renshaw BR, Douangpanya J, et al. Interleukin-36 (IL-36) ligands require processing for full agonist agonist (IL-36a, IL-36b, and IL-36g) or antagonist (IL-36Ra) activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2011; 286:42594-602.
Vigne S, Palmer G, Martin P, et al. IL-36 signaling amplifies Th1 responses by enhancing proliferation and Th1 polarization of naive CD4+ T cells. Blood 2012; 120:3478-87.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.