ITCH Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q96J02 |
| Other Accession | NP_001244066, 380420335 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
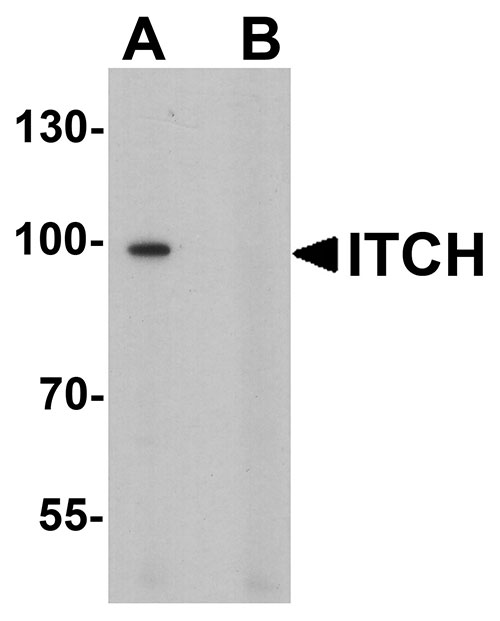
| Calculated MW | Predicted: 99 kDa Observed: 99 kDa |
| Application Notes | ITCH antibody can be used for detection of ITCH by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml. |
| Gene ID | 83737 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | ITCH; ITCH antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive. At least three isoforms of ITCH are known to exist; this antibody only recognizes the two longest isoforms. This antibody is predicted to not cross-react with other members of the Nedd4 protein family. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | ITCH antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | ITCH Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | ITCH |
|---|---|
| Function | Acts as an Acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which accepts ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and then directly transfers the ubiquitin to targeted substrates (PubMed:11046148, PubMed:14602072, PubMed:15051726, PubMed:16387660, PubMed:17028573, PubMed:18718448, PubMed:18718449, PubMed:19116316, PubMed:19592251, PubMed:19881509, PubMed:20068034, PubMed:20392206, PubMed:20491914, PubMed:23146885, PubMed:24790097, PubMed:25631046). Catalyzes 'Lys-29'-, 'Lys-48'- and 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin conjugation (PubMed:17028573, PubMed:18718448, PubMed:19131965, PubMed:19881509). Involved in the control of inflammatory signaling pathways (PubMed:19131965). Essential component of a ubiquitin-editing protein complex, comprising also TNFAIP3, TAX1BP1 and RNF11, that ensures the transient nature of inflammatory signaling pathways (PubMed:19131965). Promotes the association of the complex after TNF stimulation (PubMed:19131965). Once the complex is formed, TNFAIP3 deubiquitinates 'Lys-63' polyubiquitin chains on RIPK1 and catalyzes the formation of 'Lys-48'-polyubiquitin chains (PubMed:19131965). This leads to RIPK1 proteasomal degradation and consequently termination of the TNF- or LPS-mediated activation of NFKB1 (PubMed:19131965). Ubiquitinates RIPK2 by 'Lys-63'-linked conjugation and influences NOD2-dependent signal transduction pathways (PubMed:19592251). Regulates the transcriptional activity of several transcription factors, and probably plays an important role in the regulation of immune response (PubMed:18718448, PubMed:20491914). Ubiquitinates NFE2 by 'Lys-63' linkages and is implicated in the control of the development of hematopoietic lineages (PubMed:18718448). Mediates JUN ubiquitination and degradation (By similarity). Mediates JUNB ubiquitination and degradation (PubMed:16387660). Critical regulator of type 2 helper T (Th2) cell cytokine production by inducing JUNB ubiquitination and degradation (By similarity). Involved in the negative regulation of MAVS-dependent cellular antiviral responses (PubMed:19881509). Ubiquitinates MAVS through 'Lys-48'-linked conjugation resulting in MAVS proteasomal degradation (PubMed:19881509). Following ligand stimulation, regulates sorting of Wnt receptor FZD4 to the degradative endocytic pathway probably by modulating PI42KA activity (PubMed:23146885). Ubiquitinates PI4K2A and negatively regulates its catalytic activity (PubMed:23146885). Ubiquitinates chemokine receptor CXCR4 and regulates sorting of CXCR4 to the degradative endocytic pathway following ligand stimulation by ubiquitinating endosomal sorting complex required for transport ESCRT-0 components HGS and STAM (PubMed:14602072, PubMed:23146885, PubMed:34927784). Targets DTX1 for lysosomal degradation and controls NOTCH1 degradation, in the absence of ligand, through 'Lys-29'-linked polyubiquitination (PubMed:17028573, PubMed:18628966, PubMed:23886940). Ubiquitinates SNX9 (PubMed:20491914). Ubiquitinates MAP3K7 through 'Lys-48'-linked conjugation (By similarity). Together with UBR5, involved in the regulation of apoptosis and reactive oxygen species levels through the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of TXNIP: catalyzes 'Lys-48'-/'Lys-63'-branched ubiquitination of TXNIP (PubMed:20068034, PubMed:29378950). ITCH synthesizes 'Lys-63'-linked chains, while UBR5 is branching multiple 'Lys-48'-linked chains of substrate initially modified (PubMed:29378950). Mediates the antiapoptotic activity of epidermal growth factor through the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of p15 BID (PubMed:20392206). Ubiquitinates BRAT1 and this ubiquitination is enhanced in the presence of NDFIP1 (PubMed:25631046). Inhibits the replication of influenza A virus (IAV) via ubiquitination of IAV matrix protein 1 (M1) through 'Lys-48'-linked conjugation resulting in M1 proteasomal degradation (PubMed:30328013). Ubiquitinates NEDD9/HEF1, resulting in proteasomal degradation of NEDD9/HEF1 (PubMed:15051726). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cytoplasm. Nucleus Early endosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Endosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Note=May be recruited to exosomes by NDFIP1 (PubMed:18819914). Localizes to plasma membrane upon CXCL12 stimulation where it co-localizes with CXCL4 (PubMed:14602072) Localization to early endosomes is increased upon CXCL12 stimulation where it co-localizes with DTX3L and CXCL4 (PubMed:24790097) |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The Itchy E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (ITCH) is a member of the Nedd4 family of HECT domain E3 ubiquitin ligases (1). HECT domain E3 ubiquitin ligases transfer ubiquitin from E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes to protein substrates, thus targeting specific proteins for lysosomal degradation. ITCH plays a role in multiple cellular processes including erythroid and lymphoid cell differentiation and the regulation of immune responses (2). In B cells, ITCH is thought to associate with latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) of Epstein-Barr virus, specifically down-regulating its activity in B cell signaling (3). Mutations in this gene are a cause of syndromic multisystem autoimmune disease (4).
References
Perry WL, Hustad CM, Swing DA, et al. The itchy locus encodes a novel ubiquitin protein ligase that is disrupted in a18H mice. Nat. Genet. 1998; 18:143-6.
Melino G, Gallagher E, Aqeilan RI, et al. Itch: a HECT-type E3 ligase regulating immunity, skin and cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2008; 15:1103-12.
Ikeda A, Caldwell RG, Longnecker R, et al. Itchy, a Nedd4 ubiquitin ligase, downregulates latent membrane protein 2A activity in B-cell signaling. J. Virol. 2003; 77:5529-34.
Matesic LE, Copeland NG, and Jenkins NA. Itchy mice: the identification of a new pathway for the development of autoimmunity. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008; 321:185-200.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.