ARF6 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P62330 |
| Other Accession | NP_001654, 4502211 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
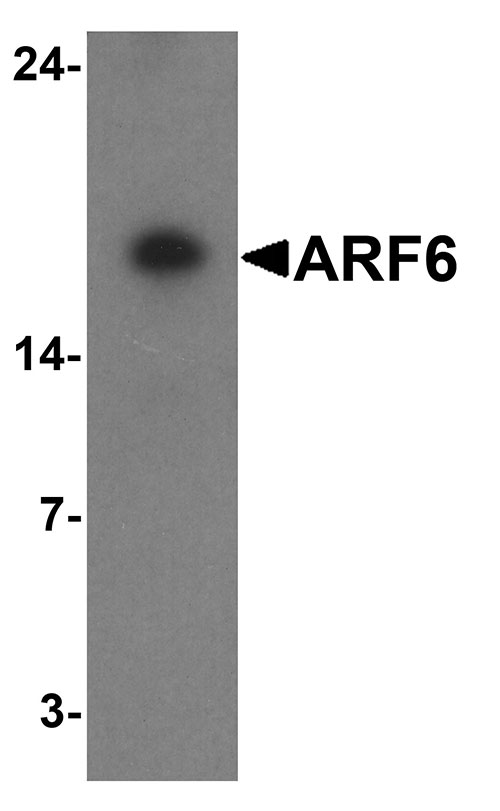
| Calculated MW | Predicted: 19 kDa Observed: 18 kDa |
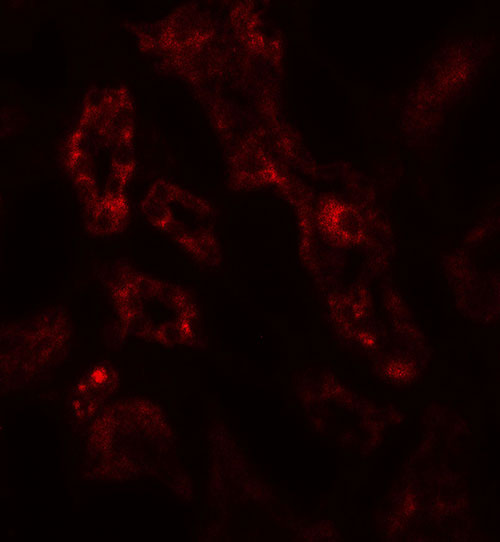
| Application Notes | ARF6 antibody can be used for detection of ARF6 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml. Antibody can also be used for Immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 382 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | ARF6; ARF6 antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | ARF6 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | ARF6 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | ARF6 {ECO:0000303|Ref.6, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:659} |
|---|---|
| Function | GTP-binding protein involved in protein trafficking that regulates endocytic recycling and cytoskeleton remodeling (PubMed:11266366, PubMed:16737952, PubMed:18400762, PubMed:21170023, PubMed:32103017, PubMed:7589240). GTP-bound form plays an important role in the transport of multiple palmitoylated proteins form the Golgi to the plasma membrane (PubMed:37461827). Required for normal completion of mitotic cytokinesis (By similarity). Plays a role in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and the formation of stress fibers (By similarity). Involved in the regulation of dendritic spine development, contributing to the regulation of dendritic branching and filopodia extension (PubMed:14978216). Potentiates the neurite outgrowth in primary neurons by interacting with the molecular adapter APBB1 (PubMed:36250347). Plays an important role in membrane trafficking, during junctional remodeling and epithelial polarization (PubMed:36017701). Regulates surface levels of adherens junction proteins such as CDH1 (By similarity). Required for NTRK1 sorting to the recycling pathway from early endosomes (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytosol. Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor. Endosome membrane; Lipid-anchor. Recycling endosome membrane; Lipid-anchor. Cell projection, filopodium membrane; Lipid- anchor. Cell projection, ruffle. Cleavage furrow. Midbody, Midbody ring. Early endosome membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P62331}; Lipid-anchor {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P62331}. Golgi apparatus, trans-Golgi network membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P62331}; Lipid-anchor {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P62331}. Note=Distributed uniformly on the plasma membrane, as well as throughout the cytoplasm during metaphase Subsequently concentrated at patches in the equatorial region at the onset of cytokinesis, and becomes distributed in the equatorial region concurrent with cleavage furrow ingression. In late stages of cytokinesis, concentrates at the midbody ring/Flemming body (PubMed:23603394). Recruitment to the midbody ring requires both activation by PSD/EFA6A and interaction with KIF23/MKLP1 (PubMed:23603394). After abscission of the intercellular bridge, incorporated into one of the daughter cells as a midbody remnant and localizes to punctate structures beneath the plasma membrane (PubMed:23603394). Recruited to the cell membrane in association with CYTH2 and ARL4C (PubMed:17398095). Colocalizes with DAB2IP at the plasma membrane and endocytic vesicles (PubMed:19948740) Myristoylation is required for proper localization to membranes: myristoylation on Lys-3 allows ARF6 to remain on membranes during the GTPase cycle (PubMed:32103017, PubMed:7589240) |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitous, with higher levels in heart, substantia nigra, and kidney. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) is a member of the ARF family, which is part of the RAS superfamily (1). The ARF proteins are small guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that stimulate the ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of cholera toxin and play a role in vesicular trafficking and as activators of phospholipase D (2). The product of this gene is localized to the plasma membrane (3), and regulates vesicular trafficking, remodelling of membrane lipids, and signaling pathways that lead to actin remodeling (4).
References
Graves RA, Tontonoz P, and Spiegelman BM. Analysis of a tissue-specific enhancer: ARF6 regulates adipogenic gene expression. Mol. Cell Biol. 1992; 12:1202-8.
Moss J and Vaughan M. Activation of toxin ADP-ribosyltransferases by eukaryotic ADP-ribosylation factors. Mol Cell Biochem. 1999; 193:153-7.
Cavenagh MM, Whitney JA, Carroll K, et al. Intracellular distribution of Arf proteins in mammalian cells. Arf6 is uniquely localized to the plasma membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1996; 271:21767-74.
Schweitzer JK, Sedgewick AE, and D’Souza-Schorey C. ARF6-mediated endocytic recycling impacts cell movement, cell division and lipid homestasis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011; 22:39-47.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.