SREBF1 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

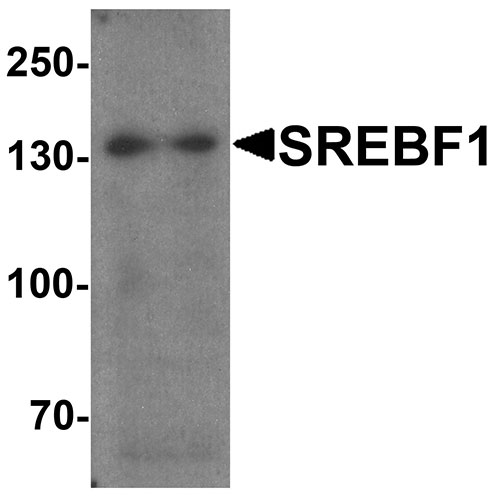
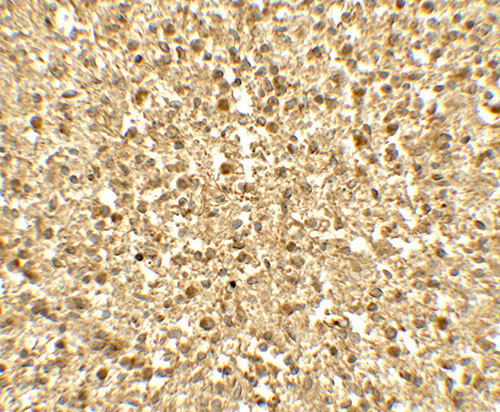
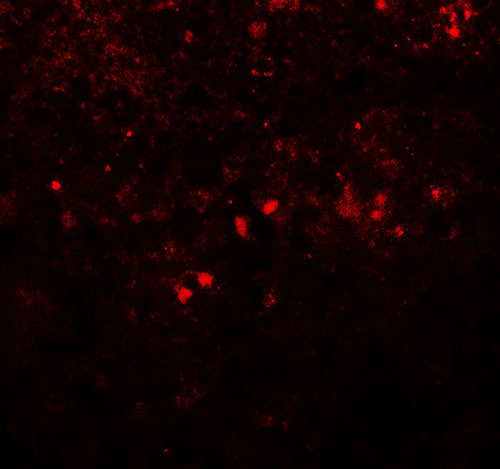
Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P36956 |
| Other Accession | NP_001005291, 52630419 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | Predicted: 129 kDa Observed: 132 kDa |
| Application Notes | SREBF1 antibody can be used for detection of SREBF1 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml. Antibody can also be used for Immunohistochemistry at 5 µg/mL. For Immunoflorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 6720 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | SREBF1; SREBF1 antibody is human and mouse reactive. At least three isoforms of SREBF1 are known to exist. SREBF1 antibody is predicted not to cross-react with SREBF2. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | SREBF1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | SREBF1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | SREBF1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:7759101, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:11289} |
|---|---|
| Function | [Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1]: Precursor of the transcription factor form (Processed sterol regulatory element- binding protein 1), which is embedded in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane (PubMed:32322062). Low sterol concentrations promote processing of this form, releasing the transcription factor form that translocates into the nucleus and activates transcription of genes involved in cholesterol biosynthesis and lipid homeostasis (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | [Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1]: Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi- pass membrane protein. Golgi apparatus membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle, COPII-coated vesicle membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WTN3}; Multi-pass membrane protein. Note=At high sterol concentrations, the SCAP-SREBP is retained in the endoplasmic reticulum. Low sterol concentrations promote recruitment into COPII-coated vesicles and transport of the SCAP-SREBP to the Golgi, where it is processed {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WTN3} [Isoform SREBP-1aDelta]: Nucleus |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in a wide variety of tissues, most abundant in liver and adrenal gland (PubMed:8402897). In fetal tissues lung and liver shows highest expression (PubMed:8402897) [Isoform SREBP-1C]: Predominantly expressed in liver and adipose tissues (PubMed:8402897). Also expressed in kidney, brain, white fat, and muscle (PubMed:8402897) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1 (SREBF1) is a transcription factor that binds to the sterol regulatory element-1 (SRE1), which is a decamer flanking the low density lipoprotein receptor gene and some genes involved in sterol biosynthesis (1). The related protein SREBF2 also binds SRE1 and activates transcription in an additive fashion to SREBF1 (2). SREBF1 is synthesized as a precursor that is attached to the nuclear membrane and endoplasmic reticulum. Following cleavage, the mature protein translocates to the nucleus and activates transcription by binding to the SRE1 (3). The SREBF1 proteins are important in the regulation of genes involved in lipid metabolism, while SREBF2 has been more closely associated with cholesterol synthesis and accumulation (4).
References
Wang X, Briggs MR, Hua X, et al. Nuclear protein that binds sterol regulatory element of low density lipoprotein receptor promoter. II. Purification and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1993; 268:14497-504.
Hua X, Yokoyama C, Wu J, et al. SREBP-2, a second basic-helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper protein that stimulates transcription by binding to a sterol regulatory element. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993; 90:11603-7.
Wang X, Sato R, Brown MS, et al. SREBP-1, a membrane-bound transcription factor released by sterol-regulated proteolysis. Cell 1994; 77:53-62.
Raghow R, Yellaturu C, Deng X, et al. SREBPs: the crossroads of physiological and pathological homeostasis. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008; 19:65-73.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.