MALT1 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

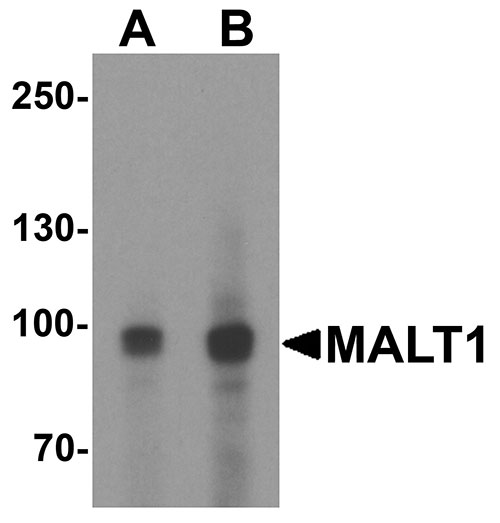
Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UDY8 |
| Other Accession | NP_006776, 5803078 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | Predicted: 91 kDa Observed: 96 kDa |
| Application Notes | MALT1 antibody can be used for detection of MALT1 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 10892 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | MALT1; MALT1 antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive. At least two isoforms of MALT1 are known to exist; this antibody will detect both isoforms. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | MALT1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | MALT1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | MALT1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:10523859, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:6819} |
|---|---|
| Function | Protease that enhances BCL10-induced activation: acts via formation of CBM complexes that channel adaptive and innate immune signaling downstream of CARD domain-containing proteins (CARD9, CARD11 and CARD14) to activate NF-kappa-B and MAP kinase p38 pathways which stimulate expression of genes encoding pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (PubMed:11262391, PubMed:18264101, PubMed:24074955). Mediates BCL10 cleavage: MALT1-dependent BCL10 cleavage plays an important role in T-cell antigen receptor-induced integrin adhesion (PubMed:11262391, PubMed:18264101). Involved in the induction of T helper 17 cells (Th17) differentiation (PubMed:11262391, PubMed:18264101). Cleaves RC3H1 and ZC3H12A in response to T-cell receptor (TCR) stimulation which releases their cooperatively repressed targets to promote Th17 cell differentiation (By similarity). Also mediates cleavage of N4BP1 in T-cells following TCR-mediated activation, leading to N4BP1 inactivation (PubMed:31133753). May also have ubiquitin ligase activity: binds to TRAF6, inducing TRAF6 oligomerization and activation of its ligase activity (PubMed:14695475). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. Nucleus Note=Shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Found in perinuclear structures together with BCL10. |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Detected at lower levels in bone marrow, thymus and lymph node, and at very low levels in colon and lung |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
MALT1 was initially identified as a novel gene that was recurrently rearranged in t(11;18)(q21;q21) mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas along with the apoptosis inhibitor protein c-IAP2 (1). MALT1, along with the proteins CARMA1 and Bcl10 form an NF-kappaB-activating complex, termed the CBM signalsome, that acts downstream of lymphocyte antigen receptors as well as many other non-lymphoid cell-surface receptors that play a role in multiple cellular functions (2,3). MALT1 has proteolytic activity, and this activity is critical for full NF-kappaB response in T cell activation (4).
References
Dielamm J, Baens M, Wlodarska I, et al. The apoptosis inhibitor gene API2 and a novel 18q gene, MLT, are recurrently rearranged in the t(11;18)(q21;q21) associated with mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas. Blood 1999; 93:3601-9.
Lin X and Wang D. The roles of CARMA1, Bcl10, and MALT1 in antigen receptor signaling. Semin. Immunol. 2004; 16:429-35.
Rosebeck S, Rehman AO, Lucas PC, et al. From MALT lymphoma to the CBM signalsome: three decades of discovery. Cell Cycle 2011; 10:2485-96.
Staal J, Bekaert T, and Beyaert R. Regulation of NF-kB signaling by caspases and MALT1 paracaspase. Cell Res. 21:40-54.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.