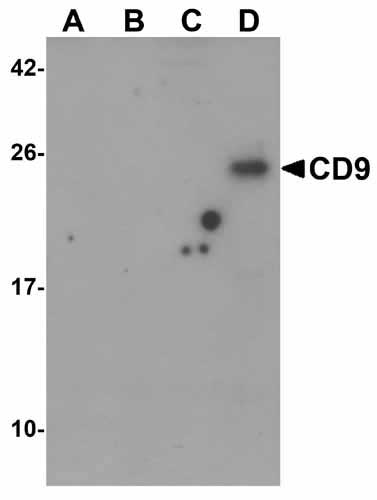
CD9 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P21926 |
| Other Accession | 4502693, NP_001760, 928 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 25416 Da |
| Application Notes | CD9 antibody can be used for Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 928 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | CD9 Antibody: CD9 molecule, MIC3, MRP-1, BTCC-1, DRAP-27, TSPAN29, TSPAN-29 |
| Precautions | CD9 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CD9 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:1840589, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:1709} |
|---|---|
| Function | Integral membrane protein associated with integrins, which regulates different processes, such as sperm-egg fusion, platelet activation and aggregation, and cell adhesion (PubMed:14575715, PubMed:18541721, PubMed:8478605). Present at the cell surface of oocytes and plays a key role in sperm-egg fusion, possibly by organizing multiprotein complexes and the morphology of the membrane required for the fusion (By similarity). In myoblasts, associates with CD81 and PTGFRN and inhibits myotube fusion during muscle regeneration (By similarity). In macrophages, associates with CD81 and beta-1 and beta-2 integrins, and prevents macrophage fusion into multinucleated giant cells specialized in ingesting complement-opsonized large particles (PubMed:12796480). Also prevents the fusion between mononuclear cell progenitors into osteoclasts in charge of bone resorption (By similarity). Acts as a receptor for PSG17 (By similarity). Involved in platelet activation and aggregation (PubMed:18541721). Regulates paranodal junction formation (By similarity). Involved in cell adhesion, cell motility and tumor metastasis (PubMed:7511626, PubMed:8478605). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Secreted, extracellular exosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P40240}. Note=Present at the cell surface of oocytes. Accumulates in the adhesion area between the sperm and egg following interaction between IZUMO1 and its receptor IZUMO1R/JUNO {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P40240} |
| Tissue Location | Detected in platelets (at protein level) (PubMed:19640571). Expressed by a variety of hematopoietic and epithelial cells (PubMed:19640571). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
CD9 Antibody: CD9 is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Like other tetraspanins, CD9 is a cell surface glycoproteins play a role in many cellular processes including differentiation, adhesion, and signal transduction (1). CD9 expression plays a critical role in the suppression of cancer cell motility and metastasis. In one study, the knockdown of CD9 expression suppressed the metastatic capacity of human breast cancer cells (2), while other results have shown the opposite effect, suggesting that different proteins associated with CD9 account for its abilities to promote or suppress metastasis (3).
References
Murayama Y, Oritani K, and Tsutsui S. Novel CD9-targeted therapies in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:3206-13.;Rappa G, Green TM, Karbanova J, Corbeil D, et al. Tetraspanin CD9 determines invasiveness and tumorigenicity of human breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015; 6:7970-91.;Zoller M. Tetraspanins: push and pull in suppressing and promoting metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009; 9:40-55.;
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.