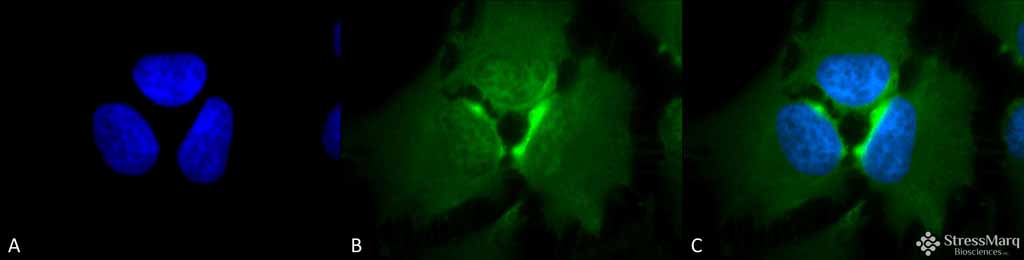
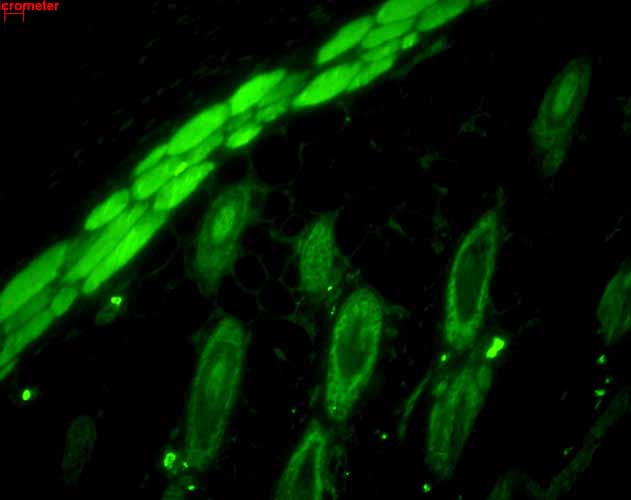
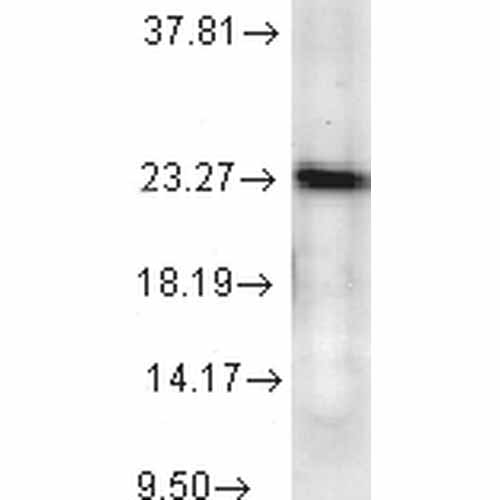
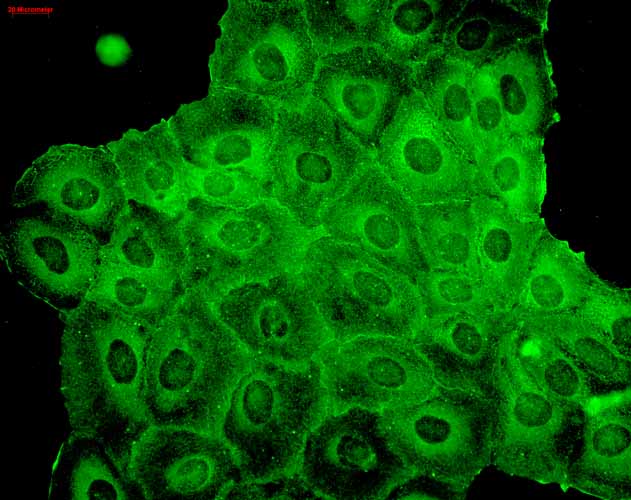
p23 Antibody
p23 Antibody, Clone JJ6
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, ICC, IP, E, AM |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q15185 |
| Other Accession | NP_006592.3 |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rabbit, Chicken, Yeast, Guinea Pig |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Description | Mouse Anti-Human p23 Monoclonal IgG1 |
| Target/Specificity | Detects ~23kDa. |
| Other Names | co chaperone p23 Antibody, PTGES3 Antibody, TEBP Antibody, telomerase binding protein p23 Antibody, unactive progesterone receptor 23kDa Antibody, HSP90 co-chaperone Antibody, Progesterone receptor complex p23 Antibody, Cytosolic prostaglandin E2 synthase Antibody |
| Clone Names | JJ6 |
| Immunogen | Recombinant human full length p23 protein |
| Purification | Protein G Purified |
| Storage | -20ºC |
| Storage Buffer | PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide |
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice or 4ºC |
| Certificate of Analysis | 0.5 µg/ml of SMC-156 was sufficient for detection of p23 in 20 µg of heat shocked cell lysate by colorimetric immunoblot analysis using Goat anti-mouse IgG:HRP as the secondary antibody. |
| Cellular Localization | Cytoplasm |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
p23 is a highly conserved ubiquitous protein, known to have an important function as a cochaperone for the HSP90 chaperoning system (1). Studies have revealed that p23 is a small protein (18 to 25 kDa) with a simple structure (2, 3). p23 does not have any structural homology with any other known proteins (1). p23 was first discovered as a part of the HSP90-progesterone receptor complex along with HSP70, p54 and p50 (1). p23 is a phosphor-protein, which is highly acidic and has an aspartic acid-rich c-terminal domain (1). Numerous studies have found p23 to be associated with other client proteins like Fes tyrosine kinase (4), the heme regulated kinase HRI (5), hsf1 transcription factor (4), aryl hydrocarbon receptor (4), telomerase (6), and Hepadnavirus reverse transcriptase (7). In spite of several years of study, the exact functional significance of p23 is still not clear (8). p23 is thought to be involved in the adenosine triphosphate–mediated HSP90 binding of client proteins (8). Since many HSP90 client proteins are involved in oncogenic survival signaling, a recent study has concluded p23 to be a promising target in leukemic apoptosis (9). HSP90 and its co-chaperone p23 are certainly among the emerging anti-tumor targets in oncology.
References
1. Johnson J.L., Beito T. G., Krco C.J. & Toft D.O. (1994) Mol Cell Biol 14: 1956-63.
2. Weikl T., Abelmann K. & Buchner J. (1999) J Mol Biol 293: 685-91.
3. Weaver A.J., Sullivan W.P., Felts S.J., Owen B.A. & Toft, D.O. (2000) J Biol Chem 275: 23045-52.
4. Nair S.C., et al. (1996) Cell Stress Chaperones 1: 237-50.
5. Xu Z., et al. (1997) Eur J Biochem 246, 461-70.
6. Holt S.E., et al. (1999) Genes Dev 13: 817-26.
7. Hu J., Toft D., Anselmo D. & Wang X. (2002) J Virol 76: 269-79.
8. Felts, S.J. & Toft D.O. (2003) Cell Stress Chaperones 8: 108-13.
9. Gausdal G., Gjertsen B.T., Fladmark K.E., Demol H., Vandekerckhove J. & Doskeland S.O. (2004) Leukemia.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.