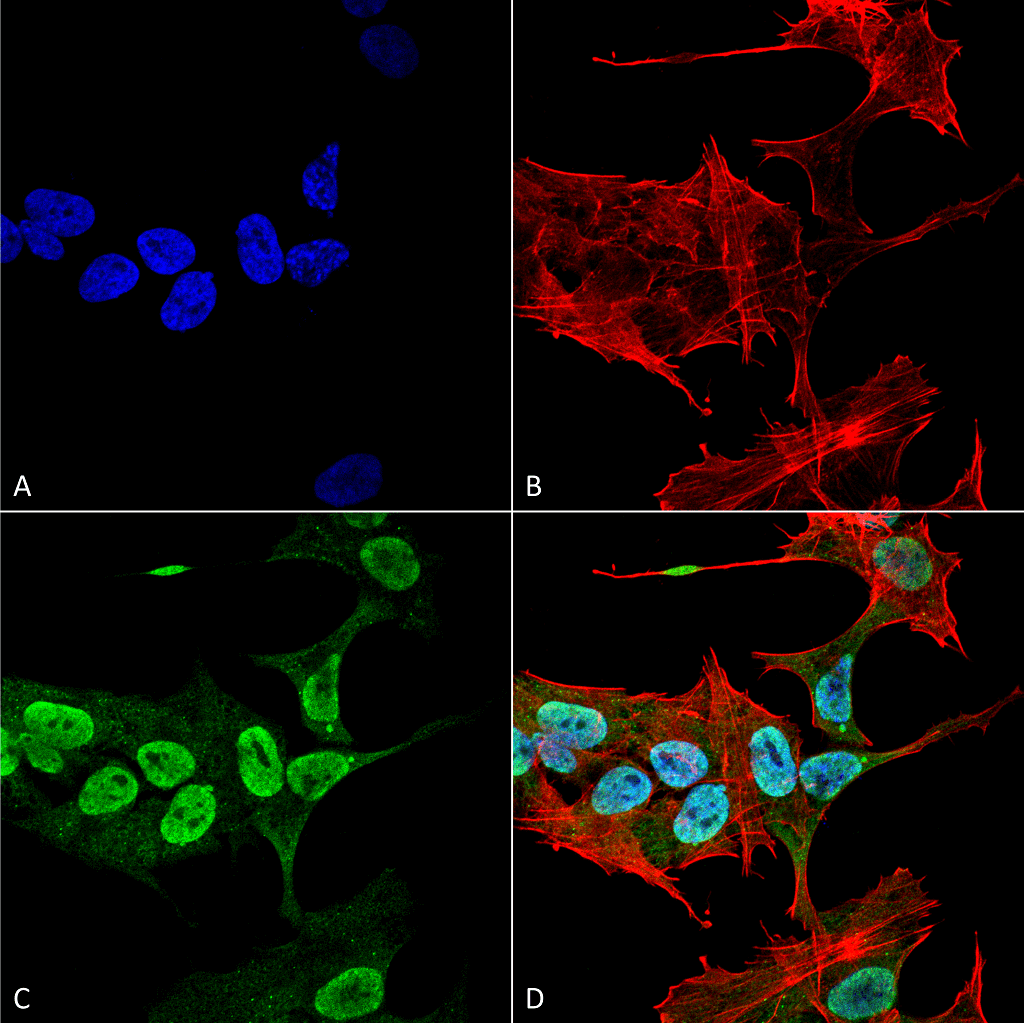
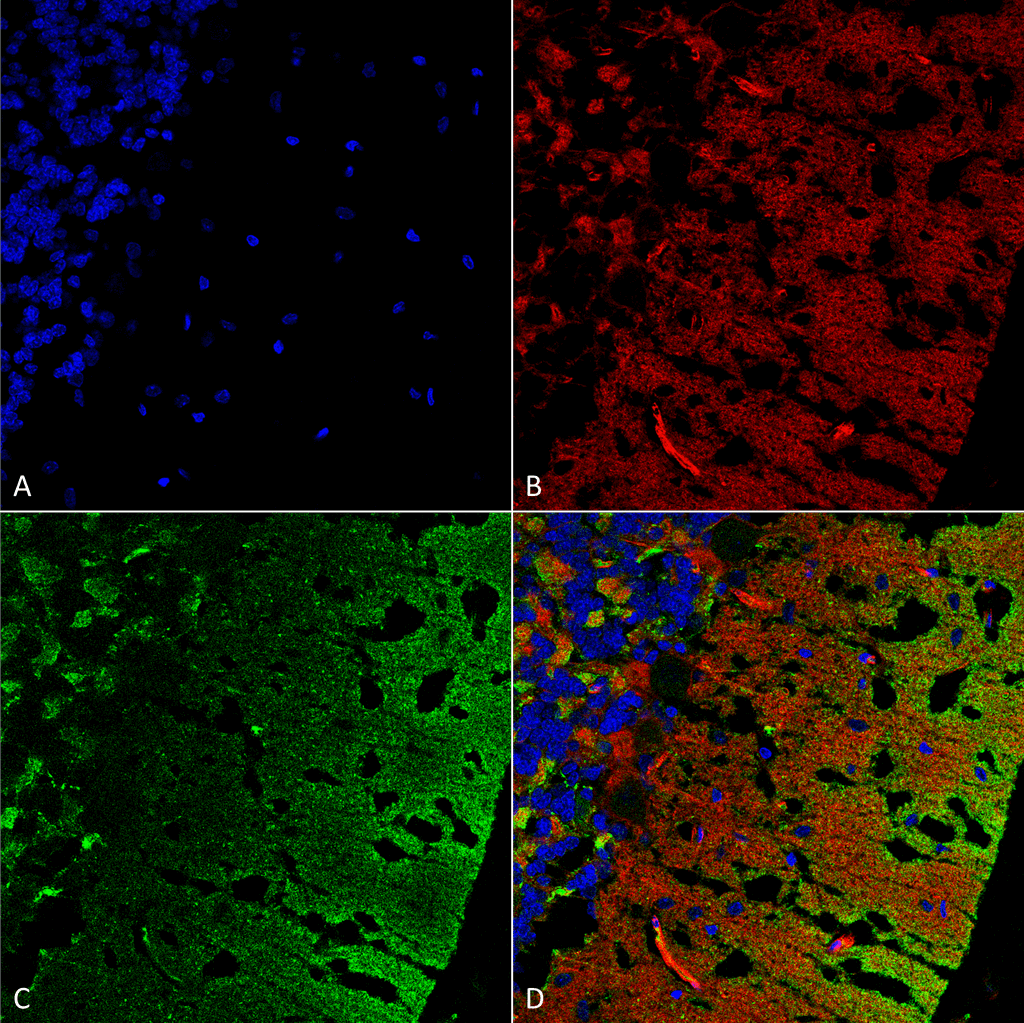
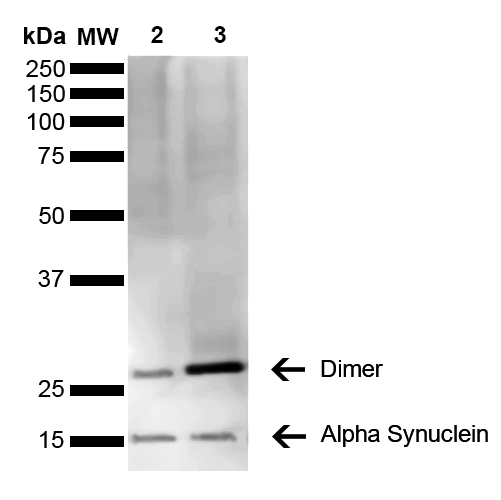
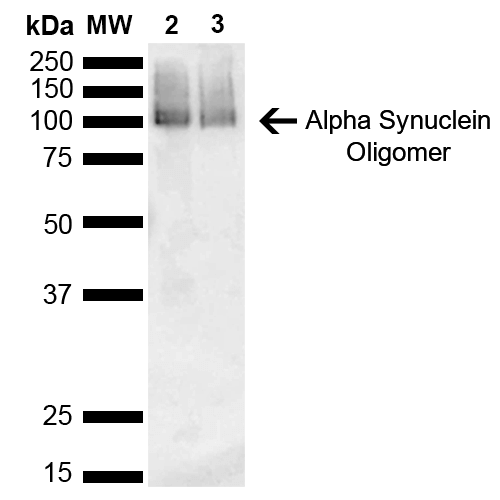
Alpha Synuclein Antibody
Alpha Synuclein Antibody, Clone 3C11
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

| Primary Accession | P37840 |
|---|---|
| Other Accession | NP_000336.1 |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Target/Specificity | Alpha Synuclein |
| Other Names | Alpha Synuclein Antibody, Non-A beta component of AD amyloid Antibody, Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor Antibody, NACP Antibody, SNCA Antibody, PARK1 Antibody, PARK 1 Antibody, alphaSYN Antibody, PARK 4 antibody, PARK4 antibody, Parkinson disease familial 1 antibody, Parkinson disease (autosomal dominant, Lewy body) 4 antibody, SYN antibody |
| Clone Names | Alpha Synuclein |
| Immunogen | Human alpha synuclein monomer |
| Purification | Protein G Purified |
| Storage | -20ºC |
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH 7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.09% Sodium azide *Storage buffer may change when conjugated |
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice or 4ºC |
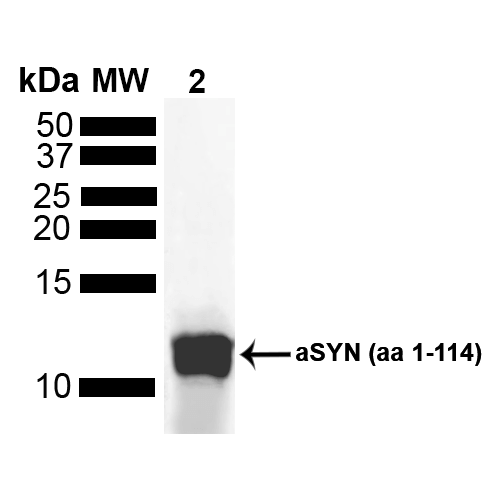
| Certificate of Analysis | A 1:1000 dilution of SMC-530 was sufficient for detection of Alpha Synuclein in 15 µg of human brain cell lysate by ECL immunoblot analysis using goat anti-mouse IgG:HRP as the secondary antibody. |
| Cellular Localization | Cytoplasm | Cytosol | Membrane | Nucleus | Cell Junction | Synapse |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Alpha-Synuclein (SNCA) is expressed predominantly in the brain, where it is concentrated in presynaptic nerve terminals (1). Alpha-synuclein is highly expressed in the mitochondria of the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, striatum and thalamus (2). Functionally, it has been shown to significantly interact with tubulin (3), and may serve as a potential microtubule-associated protein. It has also been found to be essential for normal development of the cognitive functions; inactivation may lead to impaired spatial learning and working memory (4). SNCA fibrillar aggregates represent the major non A-beta component of Alzheimers disease amyloid plaque, and a major component of Lewy body inclusions, and Parkinson's disease. Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive accumulation in selected neurons of protein inclusions containing alpha-synuclein and ubiquitin (5, 6).
References
1. “Genetics Home Reference: SNCA”. US National Library of Medicine. (2013).
2. Zhang L., et al. (2008) Brain Res. 1244: 40-52.
3. Alim M.A., et al. (2002) J Biol Chem. 277(3): 2112-2117.
4. Kokhan V.S., Afanasyeva M.A., Van'kin G. (2012) Behav. Brain. Res. 231(1): 226-230.
5. Spillantini M.G., et al. (1997) Nature. 388(6645): 839-840.
6. Mezey E., et al. (1998) Nat Med. 4(7): 755-757.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.