Anti-Myosin 6 (Rabbit) Antibody
Myosin-6 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND
| Host | Rabbit |
|---|---|
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Target Species | Swine |
| Reactivity | Pig, Human |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
Application
| WB, E, I, LCI |
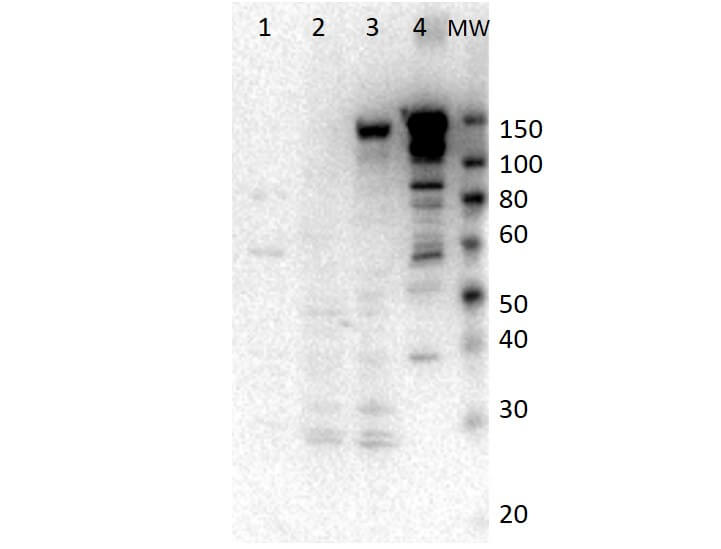
| Application Note | Myosin-6 antibody has been tested by western blot. For western blots expect a band of approximately 150 kDa in size corresponding to full length and ~85kDa and ~60kDa for truncated myosin-6 protein. Specific conditions for reactivity should be optimized by the end user. This antibody is suitable for use in ELISA. |
| Physical State | Liquid (sterile filtered) |
| Buffer | 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2 |
| Immunogen | Anti-Myosin-6 was prepared from whole rabbit serum produced by repeated immunizations with full length myosin-6 construct expressed in SF9 insect cells corresponding to porcine myosyn-6 protein. |
| Preservative | 0.01% (w/v) Sodium Azide |
| Gene ID | 397085 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | 397085 |
| Purity | Anti-Myosin-6 is directed against the myosin-6 protein. The product was prepared from monospecific antiserum by delipidation and defibrination. A BLAST analysis was used to suggest reactivity with 94% human Myosin VI. Cross-reactivity with myosin6 from other sources have not been determined. |
| Storage Condition | Store vial at -20° C prior to opening. Aliquot contents and freeze at -20° C or below for extended storage. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4° C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use. |
| Precautions Note | This product is for research use only and is not intended for therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Name | MYO6 |
|---|---|
| Function | Myosins are actin-based motor molecules with ATPase activity (By similarity). Unconventional myosins serve in intracellular movements (By similarity). Myosin 6 is a reverse-direction motor protein that moves towards the minus-end of actin filaments (By similarity). Has slow rate of actin-activated ADP release due to weak ATP binding (PubMed:15944696). Functions in a variety of intracellular processes such as vesicular membrane trafficking and cell migration (PubMed:16917816). Required for the structural integrity of the Golgi apparatus via the p53-dependent pro-survival pathway (By similarity). Appears to be involved in a very early step of clathrin-mediated endocytosis in polarized epithelial cells (By similarity). Together with TOM1, mediates delivery of endocytic cargo to autophagosomes thereby promoting autophagosome maturation and driving fusion with lysosomes (By similarity). Links TOM1 with autophagy receptors, such as TAX1BP1; CALCOCO2/NDP52 and OPTN (By similarity). May act as a regulator of F-actin dynamics (PubMed:7929586). As part of the DISP complex, may regulate the association of septins with actin and thereby regulate the actin cytoskeleton (By similarity). May play a role in transporting DAB2 from the plasma membrane to specific cellular targets (By similarity). May play a role in the extension and network organization of neurites (By similarity). Required for structural integrity of inner ear hair cells (By similarity). Required for the correct localization of CLIC5 and RDX at the stereocilium base (By similarity). Modulates RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Golgi apparatus, trans-Golgi network membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9UM54}; Peripheral membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9UM54}. Golgi apparatus {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9UM54}. Nucleus {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9UM54} Cytoplasm, perinuclear region {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9UM54}. Membrane, clathrin-coated pit {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9UM54}. Cytoplasmic vesicle, clathrin-coated vesicle {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9UM54}. Cell projection, filopodium {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9UM54}. Cell projection, ruffle membrane. Cell projection, microvillus {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9UM54}. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Note=Also present in endocytic vesicles (PubMed:16917816). Translocates from membrane ruffles, endocytic vesicles and cytoplasm to Golgi apparatus, perinuclear membrane and nucleus through induction by p53 and p53-induced DNA damage (By similarity). Recruited into membrane ruffles from cell surface by EGF- stimulation (By similarity). Colocalizes with DAB2 in clathrin-coated pits/vesicles (By similarity). Colocalizes with OPTN at the Golgi complex and in vesicular structures close to the plasma membrane (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9I8D1, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9UM54, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16917816} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in all tissues examined including kidney cortex, intestinal mucosa, liver, lung, heart, jowl muscle, brain cortex and medulla, and in the epithelial cell line, LLC-PK1 (at protein level) (PubMed:7929586). In the kidney, located to the brush border of adult kidney proximal tubule cells (PubMed:7929586) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Myosin VI is a myosin superfamily member with unique and intriguing features that allow it to fill a still-expanding number of cell biological roles. This actin-based motor produces force that acts towards the minus end of actin filaments, which is the opposite direction to all other characterized myosins. In mammalian cells, myosin VI is localized to endocytic vesicles, membrane ruffles, the cytosol and the Golgi complex. Its motor function is essential for several physiological functions of the cell, including normal rates of endocytosis, maintenance of Golgi morphology and protein secretion. Myosin VI regulates epithelial cell migration and plays a role in the maintenance of adhesive cellular contacts within epithelial cell layers. It is highly expressed in ovarian cancers and prostate cancers and its expression level, which is upregulated by DNA damage in a p53-dependent manner, correlates with the potential of the tumor to disseminate. More recently, myosin VI has been found involved in EGFR endocytosis through a clathrin dependent mechanism.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.