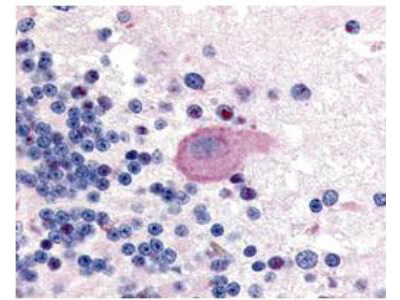
Anti-Huntington pS421 (RABBIT) Antibody
Huntington phospho S421 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

| Host | Rabbit |
|---|---|
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Target Species | Human |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
Application
| WB, IHC, E, I, LCI |
| Application Note | Anti-Huntingtin pS421 antibody has been tested for use in ELISA, immunohistochemistry, and by western blot. Specific conditions for reactivity should be optimized by the end user. Expect bands at approximately 350 kDa and 200 kDa in size corresponding to full-length Huntingtin protein and truncated (hypothetical) Huntingtin protein, respectively, by western blotting in the appropriate cell lysate or extract. This antibody is specific for the phosphorylated form of Huntingtin protein at the pS421 residue. The identity of lower molecular bands ~130 kDa is not known. |
| Physical State | Liquid (sterile filtered) |
| Buffer | 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2 |
| Immunogen | Huntingtin pS421 Antibody was prepared from whole rabbit serum produced by repeated immunizations with a synthetic peptide corresponding to an internal region near aa 400-425 of Human Huntington Disease Protein. |
| Preservative | 0.01% (w/v) Sodium Azide |
| Gene ID | 3064 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | 3064 |
| Purity | Anti-Huntingtin pS421 is an affinity purified antibody produced by immunoaffinity chromatography using phospho peptide coupled to agarose beads followed by solid phase adsorption(s) against non-phospho peptide and non-specific peptide to remove any unwanted reactivities. This antibody is specific for phosphorylated human Huntington protein at the pS421 residue. BLAST analysis indicates 100 % homology of the immunizing sequence with Huntington homologues from chimpanzee, pig and chicken. Cross reactivity with Huntington protein homologues from mouse and rat may also occur as sequence homology varies by one amino acid residue in this sequence. Reactivity with Huntington protein from other sources is not known. Minimal reactivity is expected with the non-phosphorylated form of the protein. |
| Storage Condition | Store vial at -20° C prior to opening. Aliquot contents and freeze at -20° C or below for extended storage. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4° C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use. |
| Precautions Note | This product is for research use only and is not intended for therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Name | HTT |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | HD, IT15 |
| Function | [Huntingtin]: May play a role in microtubule-mediated transport or vesicle function. |
| Cellular Location | [Huntingtin]: Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Early endosome. Note=The mutant Huntingtin protein colocalizes with AKAP8L in the nuclear matrix of Huntington disease neurons. Shuttles between cytoplasm and nucleus in a Ran GTPase- independent manner (PubMed:15654337). Recruits onto early endosomes in a Rab5- and HAP40-dependent fashion (PubMed:16476778) |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in the brain cortex (at protein level). Widely expressed with the highest level of expression in the brain (nerve fibers, varicosities, and nerve endings). In the brain, the regions where it can be mainly found are the cerebellar cortex, the neocortex, the striatum, and the hippocampal formation |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Huntingtin (also known as Huntington's disease protein, Htt and HD protein) is the protein product of a disease gene linked to Huntington's disease, a neuro-degenerative disorder characterized by loss of striatal neurons. This may be caused by an expanded, unstable trinucleotide repeat in the huntingtin gene, which translates as a polyglutamine repeat in the protein product (see partial protein sequence below). The huntingtin gene locus is large, spanning 180 kb and consisting of 67 exons. It is expressed as 2 alternatively polyadenylated forms displaying different relative abundance in various fetal and adult tissues. The genetic defect leading to Huntington's disease may not necessarily eliminate transcription, but may confer a new property on the mRNA or alter the function of the protein. One candidate is the huntingtin-associated protein-1, highly expressed in brain, which has increased affinity for huntingtin protein with expanded polyglutamine repeats. Normal huntingtin protein shows a cytoplasmic localization. This protein is widely expressed with the highest level of expression in the brain (nerve fibers, varicosities, and nerve endings). In the brain, the regions where it can be mainly found are the cerebellar cortex, the neocortex, the striatum, and the hippocampal formation.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.