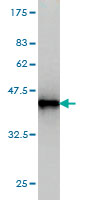
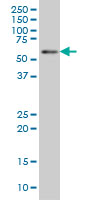
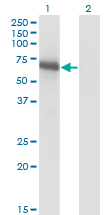
BIN1 Antibody (monoclonal) (M01)
Mouse monoclonal antibody raised against a partial recombinant BIN1.
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O00499 |
| Other Accession | NM_004305 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1 Kappa |
| Clone Names | 1H1 |
| Calculated MW | 64699 Da |
| Gene ID | 274 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Myc box-dependent-interacting protein 1, Amphiphysin II, Amphiphysin-like protein, Box-dependent myc-interacting protein 1, Bridging integrator 1, BIN1, AMPHL |
| Target/Specificity | BIN1 (NP_004296, 355 a.a. ~ 454 a.a) partial recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:500~1000 |
| Format | Clear, colorless solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2 . |
| Storage | Store at -20°C or lower. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Precautions | BIN1 Antibody (monoclonal) (M01) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This gene encodes several isoforms of a nucleocytoplasmic adaptor protein, one of which was initially identified as a MYC-interacting protein with features of a tumor suppressor. Isoforms that are expressed in the central nervous system may be involved in synaptic vesicle endocytosis and may interact with dynanim, synaptojanin, endophilin, and clathrin. Isoforms that are expressed in muscle and ubiquitously expressed isoforms localize to the cytoplasm and nucleus and activate a caspase-independent apoptotic process. Studies in mouse suggest that this gene plays an important role in cardiac muscle development. Alternate splicing of the gene results in ten transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Aberrant splice variants expressed in tumor cell lines have also been described.
References
Genetic variation and neuroimaging measures in Alzheimer disease. Biffi A, et al. Arch Neurol, 2010 Jun. PMID 20558387.Genome-wide analysis of genetic loci associated with Alzheimer disease. Seshadri S, et al. JAMA, 2010 May 12. PMID 20460622.Association of genetic variants with hemorrhagic stroke in Japanese individuals. Yoshida T, et al. Int J Mol Med, 2010 Apr. PMID 20198315.BIN1 localizes the L-type calcium channel to cardiac T-tubules. Hong TT, et al. PLoS Biol, 2010 Feb 16. PMID 20169111.Phenotype of a patient with recessive centronuclear myopathy and a novel BIN1 mutation. Claeys KG, et al. Neurology, 2010 Feb 9. PMID 20142620.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.