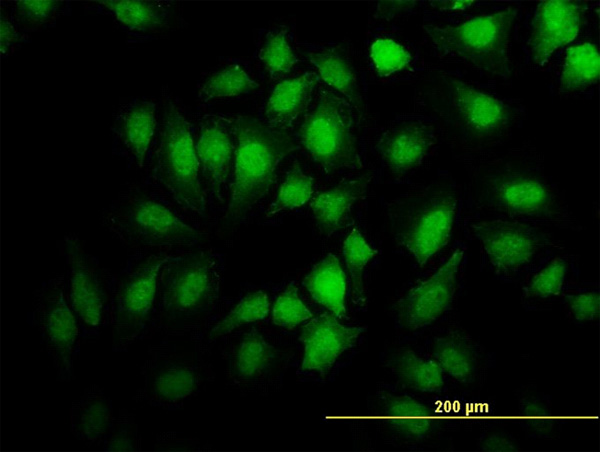
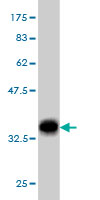
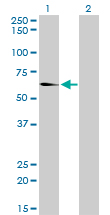
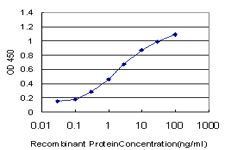
EHD2 Antibody (monoclonal) (M01)
Mouse monoclonal antibody raised against a partial recombinant EHD2.
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9NZN4 |
| Other Accession | NM_014601 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1 Kappa |
| Clone Names | 2D8 |
| Calculated MW | 61161 Da |
| Gene ID | 30846 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | EH domain-containing protein 2, PAST homolog 2, EHD2, PAST2 |
| Target/Specificity | EHD2 (NP_055416, 365 a.a. ~ 427 a.a) partial recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:500~1000 IF~~1:50~200 E~~N/A |
| Format | Clear, colorless solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2 . |
| Storage | Store at -20°C or lower. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Precautions | EHD2 Antibody (monoclonal) (M01) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This gene encodes a member of the EH domain-containing protein family. These proteins are characterized by a C-terminal EF-hand domain, a nucleotide-binding consensus site at the N terminus and a bipartite nuclear localization signal. The encoded protein interacts with the actin cytoskeleton through an N-terminal domain and also binds to an EH domain-binding protein through the C-terminal EH domain. This interaction appears to connect clathrin-dependent endocytosis to actin, suggesting that this gene product participates in the endocytic pathway.
References
EH domain proteins regulate cardiac membrane protein targeting. Gudmundsson H, et al. Circ Res, 2010 Jul 9. PMID 20489164.Architectural and mechanistic insights into an EHD ATPase involved in membrane remodelling. Daumke O, et al. Nature, 2007 Oct 3. PMID 17914359.Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes. Kimura K, et al. Genome Res, 2006 Jan. PMID 16344560.C-terminal EH-domain-containing proteins: consensus for a role in endocytic trafficking, EH? Naslavsky N, et al. J Cell Sci, 2005 Sep 15. PMID 16155252.The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC). Gerhard DS, et al. Genome Res, 2004 Oct. PMID 15489334.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.