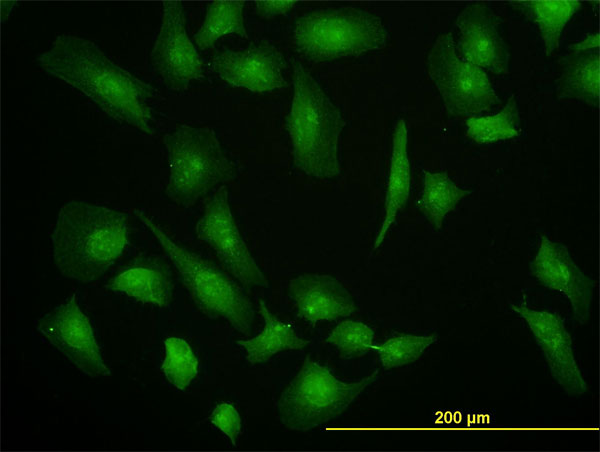
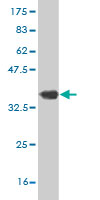
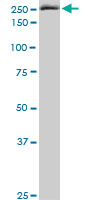
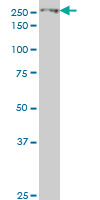
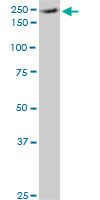
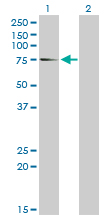
EIF4G1 Antibody (monoclonal) (M10)
Mouse monoclonal antibody raised against a partial recombinant EIF4G1.
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IF |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q04637 |
| Other Accession | NM_182917 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG2b Kappa |
| Clone Names | 2A9 |
| Calculated MW | 175491 Da |
| Gene ID | 1981 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1, eIF-4-gamma 1, eIF-4G 1, eIF-4G1, p220, EIF4G1, EIF4F, EIF4G, EIF4GI |
| Target/Specificity | EIF4G1 (NP_886553, 1500 a.a. ~ 1599 a.a) partial recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:500~1000 IF~~1:50~200 |
| Format | Clear, colorless solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2 . |
| Storage | Store at -20°C or lower. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Precautions | EIF4G1 Antibody (monoclonal) (M10) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the multi-subunit protein complex EIF4F. This complex facilitates the recruitment of mRNA to the ribosome, which is a rate-limiting step during the initiation phase of protein synthesis. The recognition of the mRNA cap and the ATP-dependent unwinding of 5'-terminal secondary structure is catalyzed by factors in this complex. The subunit encoded by this gene is a large scaffolding protein that contains binding sites for other members of the EIF4F complex. A domain at its N-terminus can also interact with the poly(A)-binding protein, which may mediate the circularization of mRNA during translation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, some of which are derived from alternative promoter usage.
References
Over-expression of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tu L, et al. Mol Cancer, 2010 Apr 16. PMID 20398343.Nuclear assortment of eIF4E coincides with shut-off of host protein synthesis upon poliovirus infection. Sukarieh R, et al. J Gen Virol, 2010 May. PMID 20053821.NAD(P)H quinone-oxydoreductase 1 protects eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4GI from degradation by the proteasome. Alard A, et al. Mol Cell Biol, 2010 Feb. PMID 20028737.HIV- 1 protease inhibits Cap- and poly(A)-dependent translation upon eIF4GI and PABP cleavage. Castell? A, et al. PLoS One, 2009 Nov 24. PMID 19956697.The Hsp90 inhibitor geldanamycin abrogates colocalization of eIF4E and eIF4E-transporter into stress granules and association of eIF4E with eIF4G. Suzuki Y, et al. J Biol Chem, 2009 Dec 18. PMID 19850929.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.