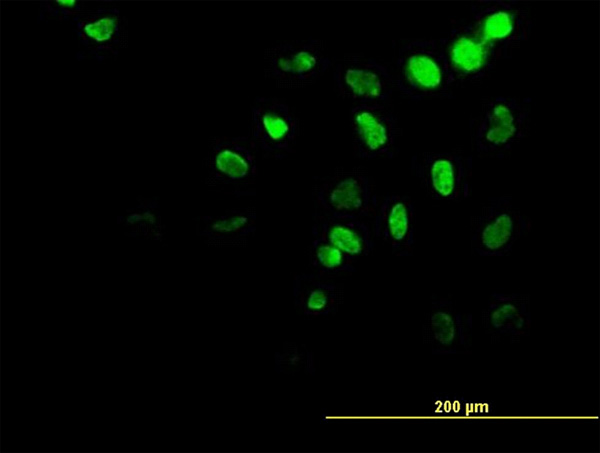
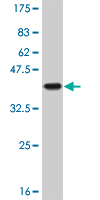
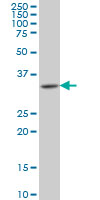
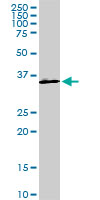
HOXA11 Antibody (monoclonal) (M08)
Mouse monoclonal antibody raised against a partial recombinant HOXA11.
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
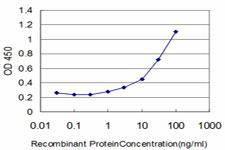
| WB, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P31270 |
| Other Accession | NM_005523 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG3 Kappa |
| Clone Names | 5A3 |
| Calculated MW | 34486 Da |
| Gene ID | 3207 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Homeobox protein Hox-A11, Homeobox protein Hox-1I, HOXA11, HOX1I |
| Target/Specificity | HOXA11 (NP_005514, 60 a.a. ~ 166 a.a) partial recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:500~1000 IF~~1:50~200 E~~N/A |
| Format | Clear, colorless solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2 . |
| Storage | Store at -20°C or lower. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Precautions | HOXA11 Antibody (monoclonal) (M08) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
In vertebrates, the genes encoding the class of transcription factors called homeobox genes are found in clusters named A, B, C, and D on four separate chromosomes. Expression of these proteins is spatially and temporally regulated during embryonic development. This gene is part of the A cluster on chromosome 7 and encodes a DNA-binding transcription factor which may regulate gene expression, morphogenesis, and differentiation. This gene is involved in the regulation of uterine development and is required for female fertility. Mutations in this gene can cause radio-ulnar synostosis with amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia.
References
HOX A10 and HOX A11 mutation scan in congenital malformations of the female genital tract. Liatsikos SA, et al. Reprod Biomed Online, 2010 Jul. PMID 20457539.Altered transmission of HOX and apoptotic SNPs identify a potential common pathway for clubfoot. Ester AR, et al. Am J Med Genet A, 2009 Dec. PMID 19938081.HoxA-11 and FOXO1A cooperate to regulate decidual prolactin expression: towards inferring the core transcriptional regulators of decidual genes. Lynch VJ, et al. PLoS One, 2009 Sep 3. PMID 19727442.DNA methylation analysis in liquid-based cytology for cervical cancer screening. Apostolidou S, et al. Int J Cancer, 2009 Dec 15. PMID 19609949.High-density association study of 383 candidate genes for volumetric BMD at the femoral neck and lumbar spine among older men. Yerges LM, et al. J Bone Miner Res, 2009 Dec. PMID 19453261.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.