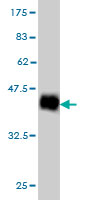
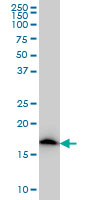
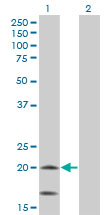
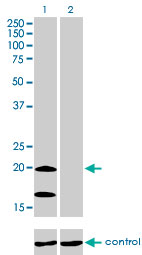
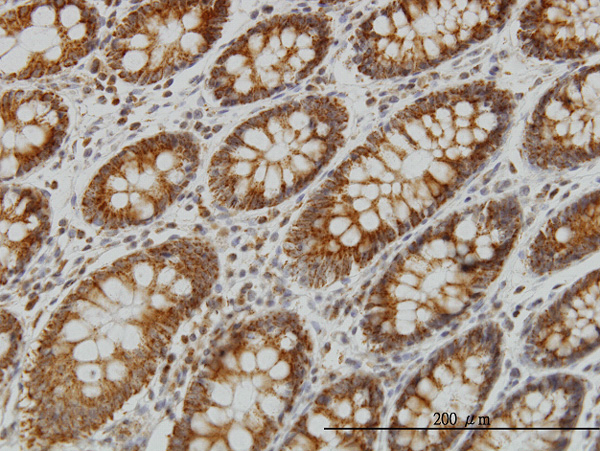
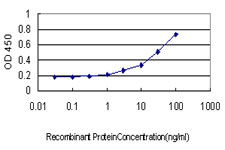
NDUFS4 Antibody (monoclonal) (M01)
Mouse monoclonal antibody raised against a partial recombinant NDUFS4.
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O43181 |
| Other Accession | NM_002495 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG2a Kappa |
| Clone Names | 1A1 |
| Calculated MW | 20108 Da |
| Gene ID | 4724 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 4, mitochondrial, Complex I-18 kDa, CI-18 kDa, Complex I-AQDQ, CI-AQDQ, NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 18 kDa subunit, NDUFS4 |
| Target/Specificity | NDUFS4 (NP_002486, 66 a.a. ~ 175 a.a) partial recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:500~1000 IHC~~1:100~500 E~~N/A |
| Format | Clear, colorless solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2 . |
| Storage | Store at -20°C or lower. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Precautions | NDUFS4 Antibody (monoclonal) (M01) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This gene encodes an accessory subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I), or NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase, the first multi-subunit enzyme complex of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Complex I plays a vital role in cellular ATP production, the primary source of energy for many crucial processes in living cells. It removes electrons from NADH and passes them by a series of different protein-coupled redox centers to the electron acceptor ubiquinone. In well-coupled mitochondria, the electron flux leads to ATP generation via the building of a proton gradient across the inner membrane. Complex I is composed of at least 41 subunits, of which 7 are encoded by the mitochondrial genome and the remainder by nuclear genes.
References
NDUFS4 mutations cause Leigh syndrome with predominant brainstem involvement. Leshinsky-Silver E, et al. Mol Genet Metab, 2009 Jul. PMID 19364667.Association study between single-nucleotide polymorphisms in 199 drug-related genes and commonly measured quantitative traits of 752 healthy Japanese subjects. Saito A, et al. J Hum Genet, 2009 Jun. PMID 19343046.Polymorphisms in mitochondrial genes and prostate cancer risk. Wang L, et al. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2008 Dec. PMID 19064571.Oxidative stress, telomere length and biomarkers of physical aging in a cohort aged 79 years from the 1932 Scottish Mental Survey. Starr JM, et al. Mech Ageing Dev, 2008 Dec. PMID 18977241.The regulation of PTC containing transcripts of the human NDUFS4 gene of complex I of respiratory chain and the impact of pathological mutations. Panelli D, et al. Biochimie, 2008 Oct. PMID 18555024.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.