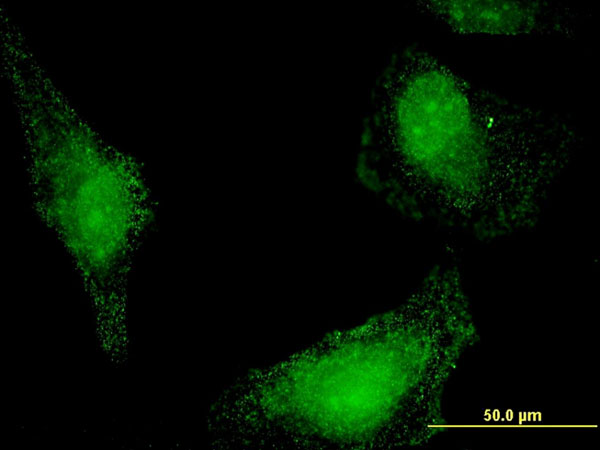
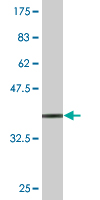
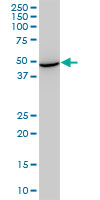
STCH Antibody (monoclonal) (M02)
Mouse monoclonal antibody raised against a partial recombinant STCH.
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P48723 |
| Other Accession | NM_006948 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG2a Kappa |
| Clone Names | 1H8 |
| Calculated MW | 51927 Da |
| Gene ID | 6782 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 13, Microsomal stress-70 protein ATPase core, Stress-70 protein chaperone microsome-associated 60 kDa protein, HSPA13, STCH |
| Target/Specificity | STCH (NP_008879.3, 375 a.a. ~ 470 a.a) partial recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:500~1000 IF~~1:50~200 E~~N/A |
| Format | Clear, colorless solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2 . |
| Storage | Store at -20°C or lower. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Precautions | STCH Antibody (monoclonal) (M02) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the heat shock protein 70 family and is found associated with microsomes. Members of this protein family play a role in the processing of cytosolic and secretory proteins, as well as in the removal of denatured or incorrectly-folded proteins. The encoded protein contains an ATPase domain and has been shown to associate with a ubiquitin-like protein.
References
Chemical manipulation of hsp70 ATPase activity regulates tau stability. Jinwal UK, et al. J Neurosci, 2009 Sep 30. PMID 19793966.New sequence variants associated with bone mineral density. Styrkarsdottir U, et al. Nat Genet, 2009 Jan. PMID 19079262.Stomach cancer-derived del223V-226L mutation of the STCH gene causes loss of sensitization to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Yamagata N, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2008 Nov 21. PMID 18793616.A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration. Lim J, et al. Cell, 2006 May 19. PMID 16713569.Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network. Rual JF, et al. Nature, 2005 Oct 20. PMID 16189514.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.