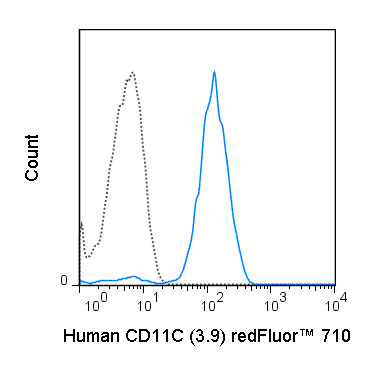
redFluor™ 710 Anti-Human CD11c (3.9) Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| FC |
|---|---|
| Isotype | Mouse IgG1, kappa |
| Concentration | 5 uL (1 ug)/test |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Formulation | 10 mM NaH2PO4, 150 mM NaCl, 0.09% NaN3, 0.1% gelatin, pH7.2 |
| Host | Mouse |
| Gene ID | 3687 |
|---|---|
| Gene Name | ITGAX |
| Alternative Name(s) | CR4, integrin _X, ITGAX |
| Format | redFluor™ 710 |
| Storage Conditions | 2-8°C protected from light |
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The 3.9 antibody reacts with human CD11c, also known as integrin alpha X. This 150 kDa cell surface glycoprotein is part of a family of integrin receptors that mediate adhesion between cells (cell-cell) and components of the extracellular matrix, e.g. fibrinogen (cell-matrix). In addition, integrins are active signaling receptors which recruit leukocytes to inflammatory sites and promote cell activation. Complete, functional integrin receptors consist of distinct combinations of integrin chains which are differentially expressed. Integrin alpha X (CD11c) assembles with Integrin beta-2 (CD18) into a receptor known as CR4 which can bind and induce signaling through ICAMs and VCAM-1 on endothelial cells and can also facilitate removal of iC3b bearing foreign cells. The 3.9 antibody is widely used as a marker for CD11c expression on dendritic cells (DC), often in parallel with markers for CD11b, for identification of developmental stages and mature subsets of this cell type. CD11c is prominently expressed on tissue macrophages, and is also detected on activated neutrophils, granulocytes, some types of activated T cells and intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL). The antibody is reported to be cross-reactive with Baboon, Chimpanzee, Cynomolgus and Rhesus CD11c.
References
Robinson BA, Estep RD, Messaoudi I, Rogers KS, and Wong SW. J. Virol. 2012. 86:2197-2211. (Flow cytometry – rhesus macaque)
Campillo-Gimenez L, Laforge M, Fay M, Brussel A, et. al. 2010. J. Virol. 84(4):1838-1846. (Flow cytometry – African green monkey, rhesus macaque)
Sadhu C, Hendrickson L, Dick KO, Potter TG, and Staunton DE. 2008. J. Immunoassay Immunochem. 29(1):42-57. (in vitro blocking)
Arndt S, Melle C, Mondal K, Klein G, von Eggeling F, and Bosserhoff A-K. 2007. J. Leukoc. Biol. 82:1466-1472. (Immunoprecipitation)
McGreal EP, Ikewaki N, Akatsu H, Morgan BP, and Gasque P. 2002. 168:5222-5232. (Immunofluorescence microscopy – frozen tissue)
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.














 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.