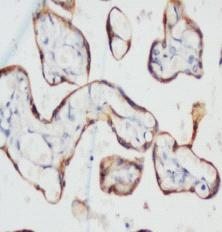
Anti-PCK Antibody (Monoclonal, C-11+PCK-26+CY-90+KS-1A3+M20+A53-B/A2)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P04264 |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | Mouse IgG2a/ IgG1 |
| Reactivity | Human, Rat |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Format | Lyophilized |
| Description | Mouse IgG monoclonal antibody for PCK detection. Tested with WB, IHC-P, IHC-F in Human;rat. No cross reactivity with other proteins. |
| Reconstitution | Add 1ml of PBS buffer will yield a concentration of 100ug/ml. |
| Gene ID | 3848 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1, 67 kDa cytokeratin, Cytokeratin-1, CK-1, Hair alpha protein, Keratin-1, K1, Type-II keratin Kb1, KRT1, KRTA |
| Calculated MW | 66039 MW KDa |
| Application Details | Immunohistochemistry(Paraffin-embedded Section), 0.1-0.5 µg/ml, Human, rat, By Heat Immunohistochemistry(Frozen Section), 0.1-0.5 µg/ml, Human, rat, - Western blot, 1-2 µg/ml, Human, rat |
| Subcellular Localization | Cell membrane . Located on plasma membrane of neuroblastoma NMB7 cells. |
| Tissue Specificity | The source of this protein is neonatal foreskin. The 67-kDa type II keratins are expressed in terminally differentiating epidermis. |
| Protein Name | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 |
| Contents | Mouse ascites fluid, 1.2% sodium acetate, 2mg BSA, with 0.01mg NaN3 as preservative. |
| Clone Names | C-11+PCK-26+CY-90+KS-1A3+M20+A53-B/A2 |
| Immunogen | mixture of several monoclonal cytokeratin clones. |
| Purification | Ascites |
| Cross Reactivity | No cross reactivity with other proteins |
| Storage | At -20˚C for one year. After r˚Constitution, at 4˚C for one month. It˚Can also be aliquotted and stored frozen at -20˚C for a longer time.Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Sequence Similarities | Belongs to the intermediate filament family. |
| Name | KRT1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | KRTA |
| Function | May regulate the activity of kinases such as PKC and SRC via binding to integrin beta-1 (ITB1) and the receptor of activated protein C kinase 1 (RACK1). In complex with C1QBP is a high affinity receptor for kininogen-1/HMWK. |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane. Cytoplasm |
| Tissue Location | The source of this protein is neonatal foreskin. The 67-kDa type II keratins are expressed in terminally differentiating epidermis |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Monoclonal anti cytokeratins are specific markers of epithelial cell differentiation and have been widely used as tools in tumor identification and classification. Monoclonal Anti Pan Cytokeratin(mixture) is a broadly reactive reagent, which recognizes epitopes present in most human epithelial tissues.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.