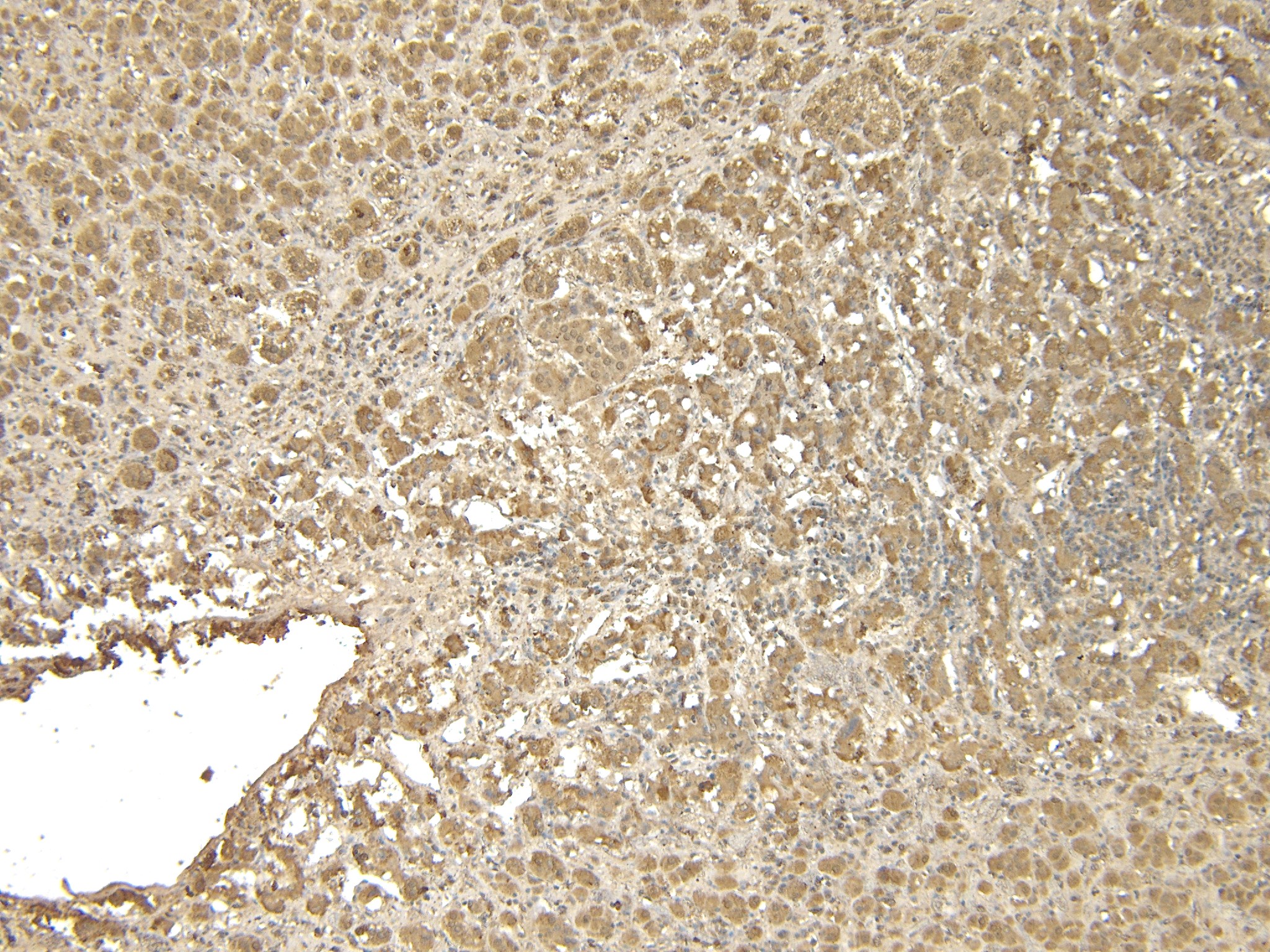
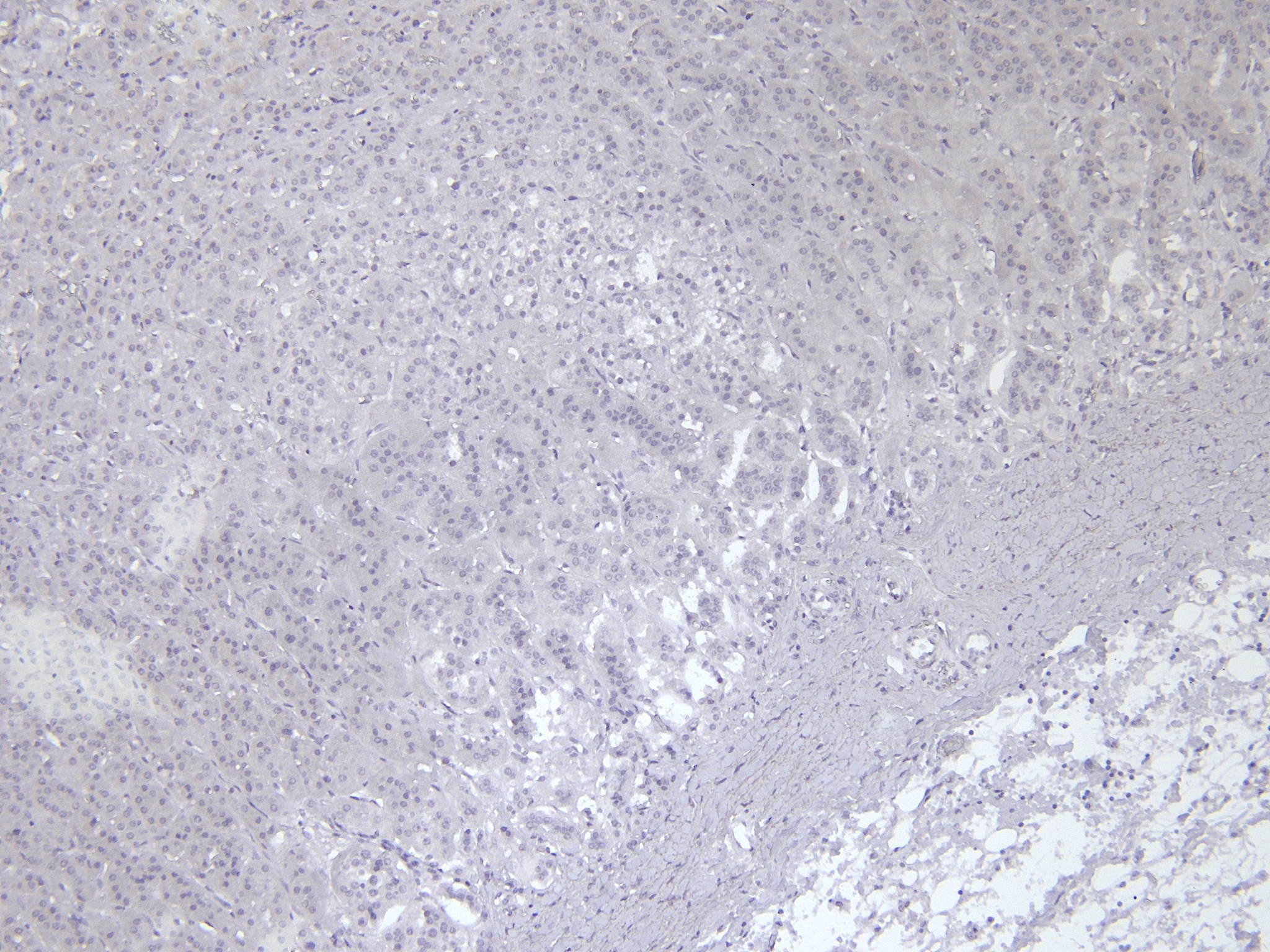
Goat Anti-VMAT2 / SLC18A2 Antibody
Peptide-affinity purified goat antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q05940 |
| Other Accession | NP_003045, 6571, 214084 (mouse), 25549 (rat) |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Predicted | Mouse, Rat, Pig, Dog |
| Host | Goat |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Concentration | 100ug/200ul |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 55713 Da |
| Gene ID | 6571 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Synaptic vesicular amine transporter, Monoamine transporter, Solute carrier family 18 member 2, Vesicular amine transporter 2, VAT2, SLC18A2, SVMT, VMAT2 |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 IHC~~1:100~500 E~~N/A |
| Format | 0.5 mg IgG/ml in Tris saline (20mM Tris pH7.3, 150mM NaCl), 0.02% sodium azide, with 0.5% bovine serum albumin |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Goat Anti-VMAT2 / SLC18A2 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | SLC18A2 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | SVMT, VMAT2 |
| Function | Electrogenic antiporter that exchanges one cationic monoamine with two intravesicular protons across the membrane of secretory and synaptic vesicles. Uses the electrochemical proton gradient established by the V-type proton-pump ATPase to accumulate high concentrations of monoamines inside the vesicles prior to their release via exocytosis. Transports a variety of catecholamines such as dopamine, adrenaline and noradrenaline, histamine, and indolamines such as serotonin (PubMed:23363473, PubMed:37914936, PubMed:38081299, PubMed:38517752, PubMed:8643547). Regulates the transvesicular monoaminergic gradient that determines the quantal size. Mediates somatodendritic dopamine release in hippocampal neurons, likely as part of a regulated secretory pathway that integrates retrograde synaptic signals (By similarity). Acts as a primary transporter for striatal dopamine loading ensuring impulse-dependent release of dopamine at the synaptic cleft (By similarity). Responsible for histamine and serotonin storage and subsequent corelease from mast cell granules (PubMed:8860238). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, synaptic vesicle membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q01827}; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q01827}; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell projection, axon {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q01827} Cell projection, dendrite {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q01827}. Note=Sorted to large dense core granules in neuroendocrine cells, presumably at the level of the trans-Golgi network. In neurons it is predominantly detected in somatodendritic tubulovesicular membranes, a distinct population of secretory vesicles that undergo calcium-dependent exocytosis in axons and dendrites upon depolarization. Localized at synaptic vesicles in axons. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q01827} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in neuronal and neuroendocrine tissues. Detected in central and peripheral nervous system in particular in axonal and dendritic processes in dopaminergic cells of substantia nigra, histaminergic neuronal cell bodies of substantia nigra and tuberomammillary nucleus, in ganglion cells of sympathetic glia and in peripheral sympathetic nerve terminals in stomach and duodenum (at protein level). Highly expressed in chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla and histamine-storing enterochromaffin-like cells of oxyntic mucosa (at protein level). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The vesicular monoamine transporter acts to accumulate cytosolic monoamines into synaptic vesicles, using the proton gradient maintained across the synaptic vesicular membrane. Its proper function is essential to the correct activity of the monoaminergic systems that have been implicated in several human neuropsychiatric disorders. The transporter is a site of action of important drugs, including reserpine and tetrabenazine (Peter et al., 1993 [PubMed 7905859]). See also SLC18A1 (MIM 193002).
References
An approach based on a genome-wide association study reveals candidate loci for narcolepsy. Shimada M, et al. Hum Genet, 2010 Oct. PMID 20677014.
Association study of 182 candidate genes in anorexia nervosa. Pinheiro AP, et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet, 2010 Jul. PMID 20468064.
Personalized smoking cessation: interactions between nicotine dose, dependence and quit-success genotype score. Rose JE, et al. Mol Med, 2010 Jul-Aug. PMID 20379614.
High regulatability favors genetic selection in SLC18A2, a vesicular monoamine transporter essential for life. Lin Z, et al. FASEB J, 2010 Jul. PMID 20181938.
In vivo measurement of vesicular monoamine transporter type 2 density in Parkinson disease with (18)F-AV-133. Okamura N, et al. J Nucl Med, 2010 Feb. PMID 20080893.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.