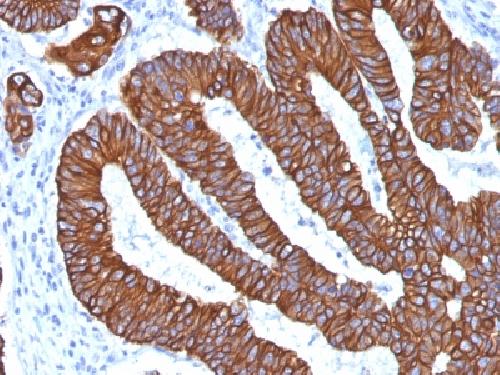
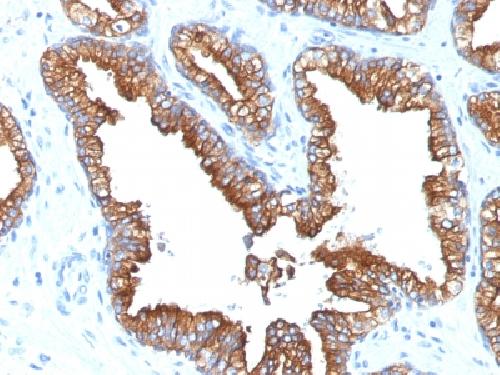
Anti-Cytokeratin 8/18 Antibody
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P05787 |
| Other Accession | 433845 (CK5), 533782, 708445 (CK8), 3856 (CK8), P05783 (CK18) |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Mouse / IgG1, kappa |
| Clone Names | KRT8.18/1346 |
| Calculated MW | 53704 Da |
| Gene ID | 3856 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | CARD2; CK8; CYK8; CYKER; Cytokeratin Endo A; DreK8; EndoA; K2C8; K8; Keratin 8; Krt 2.8; KRT8; Type-II Keratin Kb8. Cell Proliferation-inducing Gene 46 Protein; CK18; CYK18 Cytokeratin Endo B; K18; Keratin-18; Kerd; KRT18 |
| Application Note | Flow Cytometry (0.5-1ug/million cells); Immunofluorescence (1-2ug/ml); ,Western Blotting (0.5-1.0ug/ml); ,Immunohistology (Formalin-fixed) (0.5-1.0ug/ml for 30 min at RT),(Staining of formalin-fixed tissues requires boiling tissue sections in 10mM Citrate Buffer, pH 6.0, for 10-20 min followed by cooling at RT for 20 minutes),Optimal dilution for a specific application should be determined. |
| Format | 200ug/ml of Ab purified from Bioreactor Concentrate by Protein A/G. Prepared in 10mM PBS with 0.05% BSA & 0.05% azide. Also available WITHOUT BSA & azide at 1.0mg/ml. |
| Storage | Store at 2 to 8°C.Antibody is stable for 24 months. |
| Precautions | Anti-Cytokeratin 8/18 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | KRT8 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CYK8 |
| Function | Together with KRT19, helps to link the contractile apparatus to dystrophin at the costameres of striated muscle. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus, nucleoplasm {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q10758}. Nucleus matrix {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q10758} |
| Tissue Location | Observed in muscle fibers accumulating in the costameres of myoplasm at the sarcolemma membrane in structures that contain dystrophin and spectrin. Expressed in gingival mucosa and hard palate of the oral cavity. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Cytokeratin 8 (CK8) belongs to the type II (or B or basic) subfamily of high molecular weight cytokeratins and exists in combination with cytokeratin 18 (CK18). This MAb recognizes all simple epithelia including glandular epithelium, for example thyroid, female breast, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, and urogenital tract including transitional epithelium. All adenocarcinomas and most squamous carcinomas are positive but keratinizing squamous carcinomas are usually negative. This antibody is useful in demonstrating the presence of Paget cells; there is very little keratin 18 in the normal epidermis so only Paget cells are stained.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.