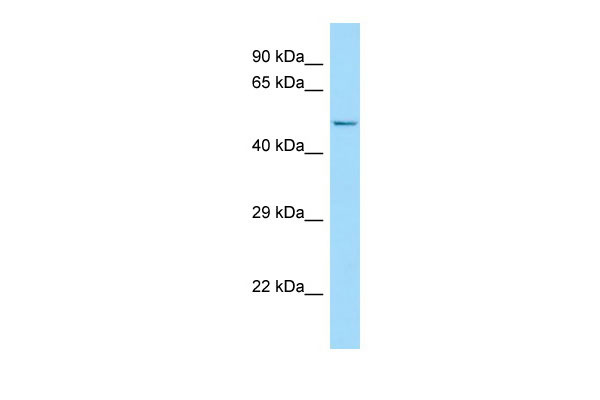
FLVCR2 Antibody - C-terminal region
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UPI3 |
| Other Accession | NM_017791, NP_060261 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Pig, Horse, Bovine, Guinea Pig, Dog |
| Predicted | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Pig, Horse, Bovine, Guinea Pig, Dog |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 57kDa |
| Gene ID | 55640 |
|---|---|
| Alias Symbol | C14orf58, CCT, FLJ20371, FLVCRL14q, EPV, PVHH, MFSD7C |
| Other Names | Feline leukemia virus subgroup C receptor-related protein 2, Calcium-chelate transporter, CCT, FLVCR2, C14orf58 |
| Format | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Add 50 ul of distilled water. Final anti-FLVCR2 antibody concentration is 1 mg/ml in PBS buffer with 2% sucrose. For longer periods of storage, store at 20°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | FLVCR2 Antibody - C-terminal region is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | FLVCR2 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:20823265, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:20105} |
|---|---|
| Function | Choline uniporter that specifically mediates choline uptake at the blood-brain-barrier (PubMed:38302740, PubMed:38778100). Responsible for the majority of choline uptake across the blood-brain- barrier from the circulation into the brain (By similarity). Choline, a nutrient critical for brain development, is a precursor of phosphatidylcholine, as well as betaine (By similarity). Also mediates transport of ethanolamine (PubMed:38778100). Choline and ethanolamine transport is not coupled with proton transport and is exclusively driven by the choline gradient across the plasma membrane (PubMed:38778100). However, the presence of an inwardly directed proton gradient enhances choline uptake (By similarity). Also acts as a heme b transporter (PubMed:20823265, PubMed:32973183). Required to regulate mitochondrial respiration processes, ATP synthesis and thermogenesis (PubMed:32973183). At low heme levels, interacts with components of electron transfer chain (ETC) complexes and ATP2A2, leading to ubiquitin-mediated degradation of ATP2A2 and inhibition of thermogenesis (PubMed:32973183). Upon heme binding, dissociates from ETC complexes to allow switching from mitochondrial ATP synthesis to thermogenesis (PubMed:32973183). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Mitochondrion membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Note=Present on both luminal (blood-facing) and abluminal (brain-facing) sides of brain endothelial cell plasma membranes, with higher luminal membrane expression (By similarity) Also localizes in mitochondria where it interacts with components of the electron transfer complexes III, IV and V (PubMed:32973183) Colocalizes with ATP2A2 at the mitochondrial-ER contact junction (PubMed:32973183). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91X85, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32973183} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in non-hematopoietic tissues, with relative abundant expression in brain, placenta, lung, liver and kidney (PubMed:20823265). Also expressed in hematopoietic tissues (fetal liver, spleen, lymph node, thymus, leukocytes and bone marrow) (PubMed:20823265). Found in acidophil cells of the pituitary that secrete growth hormone and prolactin (at protein level) (PubMed:14729055). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
References
Brasier G.,et al.Exp. Cell Res. 293:31-42(2004).
Brown J.,et al.Submitted (DEC-2001) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Ota T.,et al.Nat. Genet. 36:40-45(2004).
Heilig R.,et al.Nature 421:601-607(2003).
Mural R.J.,et al.Submitted (JUL-2005) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.