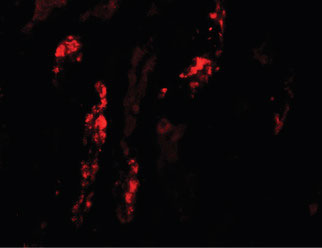
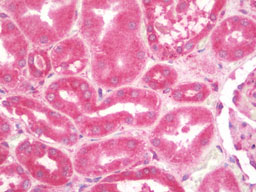
KANK1 Antibody (N-Terminus)
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q14678 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 147kDa |
| Dilution | IF (20 µg/ml), IHC-P (10 µg/ml), WB (1 µg/ml) |
| Gene ID | 23189 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | KN motif and ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 1, Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 15, Kidney ankyrin repeat-containing protein, KANK1, ANKRD15, KANK, KIAA0172 |
| Target/Specificity | Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. The lower molecular weight band seen in the immunoblot is thought to be non-specific. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Long term: -20°C; Short term: +4°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | KANK1 Antibody (N-Terminus) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | KANK1 (HGNC:19309) |
|---|---|
| Function | Adapter protein that links structural and signaling protein complexes positioned to guide microtubule and actin cytoskeleton dynamics during cell morphogenesis (PubMed:22084092, PubMed:24120883). At focal adhesions (FAs) rims, organizes cortical microtubule stabilizing complexes (CMSCs) and directly interacts with major FA component TLN1, forming macromolecular assemblies positioned to control microtubule-actin crosstalk at the cell edge (PubMed:24120883, PubMed:27410476). Recruits KIF21A in CMSCs at axonal growth cones and regulates axon guidance by suppressing microtubule growth without inducing microtubule disassembly once it reaches the cell cortex (PubMed:24120883). Interacts with ARFGEF1 and participates in establishing microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) orientation and directed cell movement in wound healing (PubMed:22084092). Regulates actin stress fiber formation and cell migration by inhibiting RHOA activation in response to growth factors; this function involves phosphorylation through PI3K/Akt signaling and may depend on the competitive interaction with 14-3-3 adapter proteins to sequester them from active complexes (PubMed:18458160, PubMed:25961457). Inhibits the formation of lamellipodia but not of filopodia; this function may depend on the competitive interaction with BAIAP2 to block its association with activated RAC1. Inhibits fibronectin-mediated cell spreading; this function is partially mediated by BAIAP2 (PubMed:19171758). In the nucleus, is involved in beta-catenin- dependent activation of transcription (PubMed:16968744). During cell division, may regulate DAAM1-dependent RHOA activation that signals centrosome maturation and chromosomal segregation. May also be involved in contractile ring formation during cytokinesis (By similarity). Potential tumor suppressor for renal cell carcinoma (Probable). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cell cortex. Cell projection, ruffle membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Note=Shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus (PubMed:16968744). Colocalizes with CMSC components at focal adhesion rims. Colocalizes with KIF21A in membrane ruffles (PubMed:19559006, PubMed:27410476). Colocalizes with RHOA at the contractile ring. Colocalizes with RHOA and DAAM1 around centrosomes {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E9Q238, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16968744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19559006, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27410476} [Isoform 2]: Cytoplasm. Nucleus Note=Shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed. Isoform 1 is predominantly expressed in heart and kidney. Isoform 2 probably is widely expressed at basic levels. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Involved in the control of cytoskeleton formation by regulating actin polymerization. Inhibits actin fiber formation and cell migration. Inhibits RhoA activity; the function involves phosphorylation through PI3K/Akt signaling and may depend on the competetive interaction with 14-3-3 adapter proteins to sequester them from active complexes. Inhibits the formation of lamellipodia but not of filopodia; the function may depend on the competetive interaction with BAIAP2 to block its association with activated RAC1. Inhibits fibronectin-mediated cell spreading; the function is partially mediated by BAIAP2. Inhibits neurite outgrowth. Involved in the establishment and persistence of cell polarity during directed cell movement in wound healing. In the nucleus, is involved in beta-catenin-dependent activation of transcription. Potential tumor suppressor for renal cell carcinoma.
References
Nagase T.,et al.DNA Res. 3:17-24(1996).
Humphray S.J.,et al.Nature 429:369-374(2004).
Mural R.J.,et al.Submitted (SEP-2005) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Sarkar S.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 277:36585-36591(2002).
Wang Y.,et al.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 330:1247-1253(2005).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.