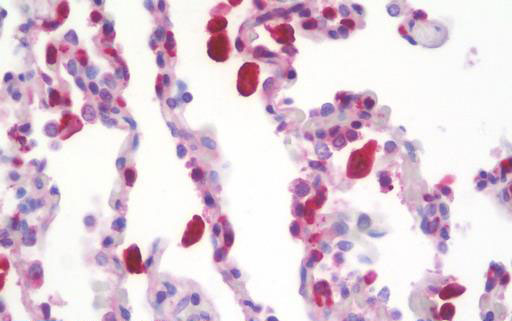
CD68 Antibody (clone KP1)
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 1
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, IP, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P34810 |
| Other Accession | 968 |
| Reactivity | Human, Rat |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Clone Names | KP1 |
| Calculated MW | 37408 Da |
| Dilution | IHC-P (5 µg/ml), |
| Gene ID | 968 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | CD68, CD68 antigen, gp110, SCARD1, CD68 molecule, LAMP4, Macrophage antigen CD68, Macrosialin |
| Target/Specificity | Recognizes the human CD68 cell surface antigen, a 110kD glycoprotein primarily expressed by macrophages and monocytes. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | PBS, 0.09% sodium azide. +4°C or -20°C, Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Precautions | CD68 Antibody (clone KP1) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CD68 |
|---|---|
| Function | Could play a role in phagocytic activities of tissue macrophages, both in intracellular lysosomal metabolism and extracellular cell-cell and cell-pathogen interactions. Binds to tissue- and organ-specific lectins or selectins, allowing homing of macrophage subsets to particular sites. Rapid recirculation of CD68 from endosomes and lysosomes to the plasma membrane may allow macrophages to crawl over selectin-bearing substrates or other cells. |
| Cellular Location | [Isoform Short]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed by blood monocytes and tissue macrophages. Also expressed in lymphocytes, fibroblasts and endothelial cells. Expressed in many tumor cell lines which could allow them to attach to selectins on vascular endothelium, facilitating their dissemination to secondary sites. |

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Could play a role in phagocytic activities of tissue macrophages, both in intracellular lysosomal metabolism and extracellular cell-cell and cell-pathogen interactions. Binds to tissue- and organ-specific lectins or selectins, allowing homing of macrophage subsets to particular sites. Rapid recirculation of CD68 from endosomes and lysosomes to the plasma membrane may allow macrophages to crawl over selectin-bearing substrates or other cells.
References
Holness C.L.,et al.Blood 81:1607-1613(1993).
Kalnine N.,et al.Submitted (JUL-2003) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Ota T.,et al.Nat. Genet. 36:40-45(2004).
Suzuki Y.,et al.Submitted (APR-2005) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Zody M.C.,et al.Nature 440:1045-1049(2006).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.














 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.