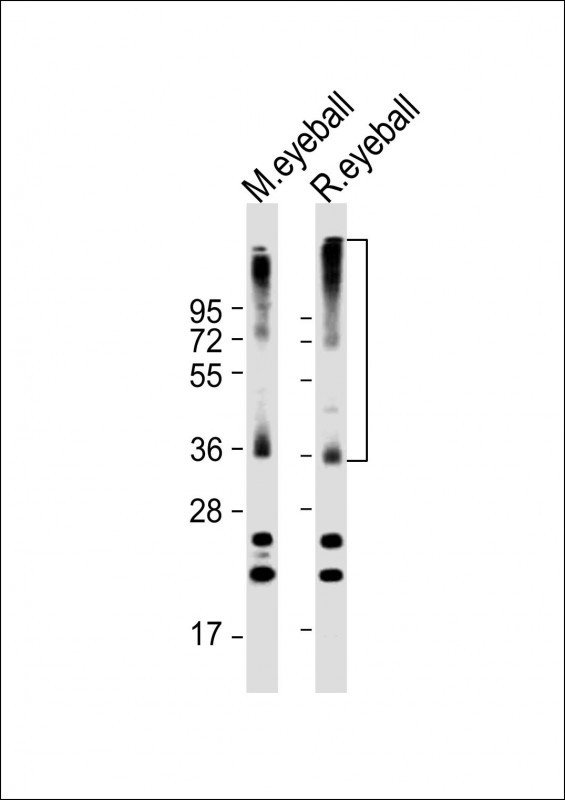
RHO Antibody (C-term)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P08100 |
| Other Accession | Q28886, NP_000530.1 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Predicted | Monkey |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 38893 Da |
| Antigen Region | 310-339 aa |
| Gene ID | 6010 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Rhodopsin, Opsin-2, RHO, OPN2 |
| Target/Specificity | This RHO antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 310-339 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human RHO. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:2000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | RHO Antibody (C-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | RHO |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | OPN2 |
| Function | Photoreceptor required for image-forming vision at low light intensity (PubMed:7846071, PubMed:8107847). Required for photoreceptor cell viability after birth (PubMed:12566452, PubMed:2215617). Light- induced isomerization of the chromophore 11-cis-retinal to all-trans- retinal triggers a conformational change that activates signaling via G-proteins (PubMed:26200343, PubMed:28524165, PubMed:28753425, PubMed:8107847). Subsequent receptor phosphorylation mediates displacement of the bound G-protein alpha subunit by the arrestin SAG and terminates signaling (PubMed:26200343, PubMed:28524165). |
| Cellular Location | Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell projection, cilium, photoreceptor outer segment. Note=Synthesized in the inner segment (IS) of rod photoreceptor cells before vectorial transport to disk membranes in the rod outer segment (OS) photosensory cilia |
| Tissue Location | Rod shaped photoreceptor cells which mediate vision in dim light |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Retinitis pigmentosa is an inherited progressive disease which is a major cause of blindness in western communities. It can be inherited as an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked recessive disorder. In the autosomal dominant form,which comprises about 25% of total cases, approximately 30% of families have mutations in the gene encoding the rod photoreceptor-specific protein rhodopsin. This is the transmembrane protein which, when photoexcited, initiates the visual transduction cascade. Defects in this gene are also one of the causes of congenital stationary night blindness.
References
Clark, G.R., et al. Ophthalmology 117(11):2169-2177(2010)
Li, S., et al. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 401(1):42-47(2010)
Pulagam, L.P., et al. J. Biol. Chem. 285(38):29446-29456(2010)
Audo, I., et al. Arch. Ophthalmol. 128(8):1036-1045(2010)
Audo, I., et al. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 51(7):3687-3700(2010)
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.