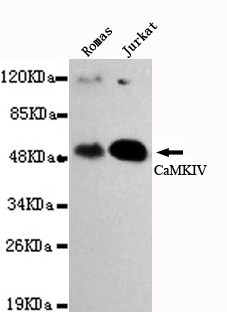
CaMKIV Antibody
Purified Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Mab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q16566 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG2a |
| Calculated MW | 55 KDa |
| Gene ID | 814 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Brain Ca(2 ) calmodulin dependent protein kinase type 4;Brain Ca(2 ) calmodulin dependent protein kinase type IV;Brain Ca -calmodulin dependent protein kinase type IV;Calcium / calmodulin dependent protein kinase type 4 catalytic chain;Calcium / calmodulin dependent protein kinase type IV catalytic chain; Calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase IV;Calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase type IV;Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV;CAM kinase 4;CAM kinase GR;CAM kinase IV;CAM kinase-GR;CaMK 4;CAMK GR;CaMK IV;CaMK4;CaMKGR;IV;KCC4_HUMAN; MGC36771. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 |
| Format | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide, pH 7.3. |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Name | CAMK4 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CAMK, CAMK-GR, CAMKIV |
| Function | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that operates in the calcium-triggered CaMKK-CaMK4 signaling cascade and regulates, mainly by phosphorylation, the activity of several transcription activators, such as CREB1, MEF2D, JUN and RORA, which play pivotal roles in immune response, inflammation, and memory consolidation. In the thymus, regulates the CD4(+)/CD8(+) double positive thymocytes selection threshold during T-cell ontogeny. In CD4 memory T-cells, is required to link T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) signaling to the production of IL2, IFNG and IL4 (through the regulation of CREB and MEF2). Regulates the differentiation and survival phases of osteoclasts and dendritic cells (DCs). Mediates DCs survival by linking TLR4 and the regulation of temporal expression of BCL2. Phosphorylates the transcription activator CREB1 on 'Ser-133' in hippocampal neuron nuclei and contribute to memory consolidation and long term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus. Can activate the MAP kinases MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK8/JNK1 and MAPK14/p38 and stimulate transcription through the phosphorylation of ELK1 and ATF2. Can also phosphorylate in vitro CREBBP, PRM2, MEF2A and STMN1/OP18. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Note=Localized in hippocampal neuron nuclei. In spermatids, associated with chromatin and nuclear matrix (By similarity). |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in brain, thymus, CD4 T-cells, testis and epithelial ovarian cancer tissue. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that operates in the calcium-triggered CaMKK-CaMK4 signaling cascade and regulates, mainly by phosphorylation, the activity of several transcription activators, such as CREB1, MEF2D, JUN and RORA, which play pivotal roles in immune response, inflammation, and memory consolidation. In the thymus, regulates the CD4(+)/CD8(+) double positive thymocytes selection threshold during T-cell ontogeny. In CD4 memory T-cells, is required to link T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) signaling to the production of IL2, IFNG and IL4 (through the regulation of CREB and MEF2). Regulates the differentiation and survival phases of osteoclasts and dendritic cells (DCs). Mediates DCs survival by linking TLR4 and the regulation of temporal expression of BCL2. Phosphorylates the transcription activator CREB1 on 'Ser-133' in hippocampal neuron nuclei and contribute to memory consolidation and long term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus. Can activate the MAP kinases MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK8/JNK1 and MAPK14/p38 and stimulate transcription through the phosphorylation of ELK1 and ATF2. Can also phosphorylate in vitro CREBBP, PRM2, MEF2A and STMN1/OP18.
References
Kitani T.,et al.J. Biochem. 115:637-640(1994).
Bland M.M.,et al.Gene 142:191-197(1994).
Mosialos G.,et al.J. Virol. 68:1697-1705(1994).
Mural R.J.,et al.Submitted (SEP-2005) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Hanissian S.H.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 268:20055-20063(1993).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.