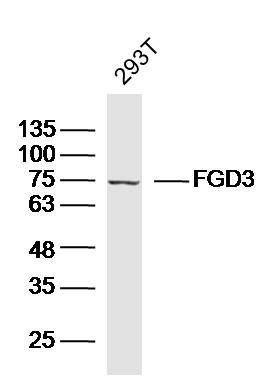
FGD3 Polyclonal Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q5JSP0 |
| Reactivity | Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 79 KDa |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human FGD3 |
| Epitope Specificity | 501-600/725 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm > cytoskeleton. |
| SIMILARITY | Contains 1 DH (DBL-homology) domain. Contains 1 FYVE-type zinc finger. Contains 2 PH domains. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | FGD1 gene mutations result in faciogenital dysplasia (FGDY, Aarskog-Scott syndrome), an X-linked developmental disorder that adversely affects the formation of multiple skeletal structures. FGD1 maps to human chromosome Xp11.21 and shares a high degree of sequence identity with the FGD2 (6p21.2) and the FGD3 (9q22.31) proteins. FGD1 encodes a guanine nucleotide exchange factor that specifically activates the Rho GTPase Cdc42. FGD2 is present in several diverse tissues during embryogenesis, suggesting a role in embryonic development. FGD3 stimulates fibroblasts to form filopodia, which are Actin microspikes formed upon the stimulation of Cdc42. All FGD family members contain equivalent signaling domains and a conserved structural organization, which strongly suggests that these signaling domains form a canonical core structure for members of the FGD family of RhoGEF proteins. These proteins control essential signals required during embryonic development. |
| Gene ID | 89846 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain-containing protein 3, Zinc finger FYVE domain-containing protein 5, FGD3, ZFYVE5 |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Storage | Store at -20 ℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 ℃. |
| Name | FGD3 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | ZFYVE5 |
| Function | Promotes the formation of filopodia. May activate CDC42, a member of the Ras-like family of Rho- and Rac proteins, by exchanging bound GDP for free GTP. Plays a role in regulating the actin cytoskeleton and cell shape (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.