ARF1 Antibody
Rabbit mAb
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
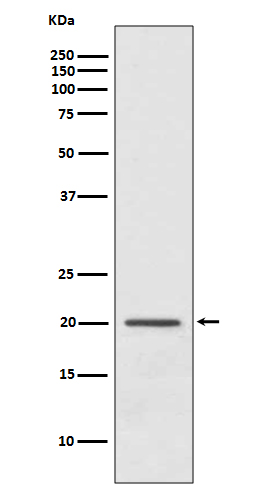
| WB, IHC, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P84077 |
| Reactivity | Rat |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Other Names | ADP Ribosylation Factor 1; ARF 1; |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Calculated MW | 20697 Da |
| Dilution | WB 1:500~1:2000 IHC 1:50~1:200 FC 1:50 |
|---|---|
| Purification | Affinity-chromatography |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human ARF1 |
| Description | Stimulate the ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of cholera toxin and play a role in vesicular trafficking as activators of phospholipase D. GTP-binding protein that functions as an allosteric activator of the cholera toxin catalytic subunit, an ADP-ribosyltransferase. Involved in protein trafficking among different compartments. |
| Storage Condition and Buffer | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. Store at +4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle. |
| Name | ARF1 |
|---|---|
| Function | Small GTPase involved in protein trafficking between different compartments (PubMed:8253837). Modulates vesicle budding and uncoating within the Golgi complex (PubMed:8253837). In its GTP-bound form, triggers the recruitment of coatomer proteins to the Golgi membrane (PubMed:8253837). The hydrolysis of ARF1-bound GTP, which is mediated by ARFGAPs proteins, is required for dissociation of coat proteins from Golgi membranes and vesicles (PubMed:8253837). The GTP- bound form interacts with PICK1 to limit PICK1-mediated inhibition of Arp2/3 complex activity; the function is linked to AMPA receptor (AMPAR) trafficking, regulation of synaptic plasticity of excitatory synapses and spine shrinkage during long-term depression (LTD) (By similarity). Plays a key role in the regulation of intestinal stem cells and gut microbiota, and is essential for maintaining intestinal homeostasis (By similarity). Also plays a critical role in mast cell expansion but not in mast cell maturation by facilitating optimal mTORC1 activation (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Golgi apparatus membrane; Lipid-anchor; Cytoplasmic side. Synapse, synaptosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P84079}. Postsynaptic density {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P84079}. Note=In the GDP-bound form, associates transiently with the membranes via its myristoylated N-terminus where guanine nucleotide-exchange factor (GEF)-mediated nucleotide exchange occurs (By similarity). Following nucleotide exchange, the GTP-bound form undergoes a conformational change, leading to the exposure of a myristoylated N-terminal amphipathic helix that provides stable membrane anchorage (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P84080} |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.