ApoA1 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P02647 |
| Other Accession | P02647, 113992 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Chicken |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgY |
| Calculated MW | 30778 Da |
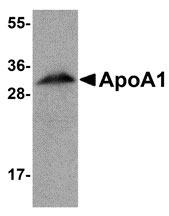
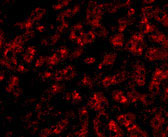
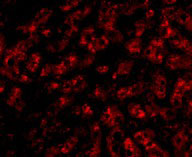
| Application Notes | ApoA1 antibody can be used for detection of ApoA1 by Western blot at 1 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunoflourescence starting at 20 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 335 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | APOA1; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | ApoA1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | ApoA1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | APOA1 (HGNC:600) |
|---|---|
| Function | Participates in the reverse transport of cholesterol from tissues to the liver for excretion by promoting cholesterol efflux from tissues and by acting as a cofactor for the lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT). As part of the SPAP complex, activates spermatozoa motility. |
| Cellular Location | Secreted. |
| Tissue Location | Major protein of plasma HDL, also found in chylomicrons. Synthesized in the liver and small intestine. The oxidized form at Met-110 and Met-136 is increased in individuals with increased risk for coronary artery disease, such as in carrier of the eNOSa/b genotype and exposure to cigarette smoking. It is also present in increased levels in aortic lesions relative to native ApoA-I and increased levels are seen with increasing severity of disease |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
ApoA1 Antibody: Apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1) is the major protein component of high density lipoprotein (HDL) in plasma. ApoA1 is synthesized in the liver and small intestine and promotes cholesterol efflux from tissues to the liver for excretion. It is a cofactor for lecithin cholesterolacyltransferase (LCAT), the enzyme responsible for the formation of most plasma cholesteryl esters. Defects in ApoA1 are associated with HDL deficiency, Tangier disease, and systemic non-neuropathic amyloidosis.
References
Sorci-Thomas MG, Prack MM, Dashti N, et al. Differential effects of dietary fat on the tissue-specific expression of the apolipoprotein A-I gene: relationship to plasma concentration of high density lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res.1989; 30:1397-403.
Lai C-Q, Parnell LD, and Ordovas JM. The APOA1/C3/A4/A5 gene cluster, lipid metabolism and cardiovascular disease risk. Curr. Opin. Lipid.2005; 16:153-66.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.