ZIP6 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q13433 |
| Other Accession | NP_001092876, 153252214 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 85047 Da |
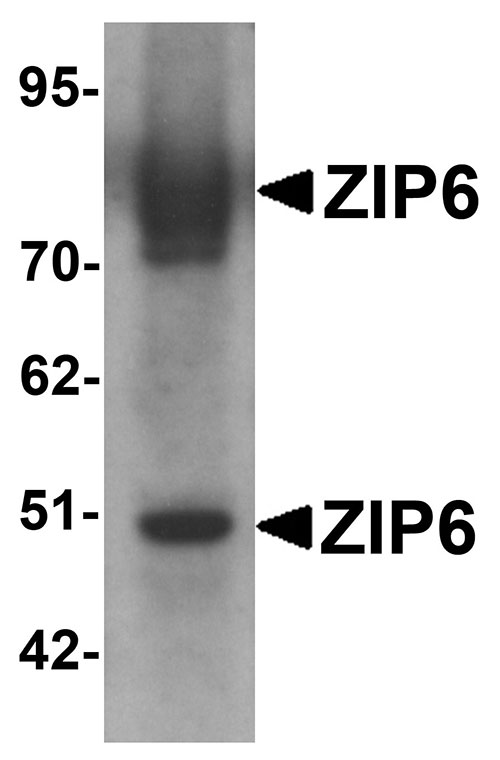
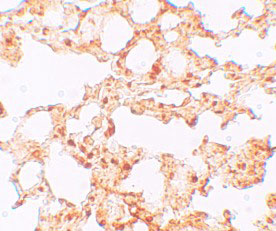
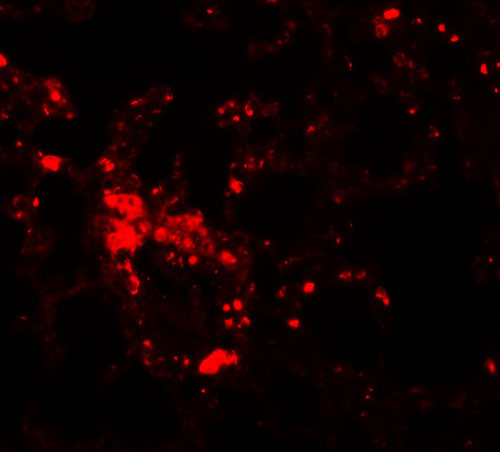
| Application Notes | ZIP6 antibody can be used for detection of ZIP6 by Western blot at 1 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 2.5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 25800 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | SLC39A6; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Antibody can be stored at 4°C up to one year. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | ZIP6 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | SLC39A6 (HGNC:18607) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | LIV1, ZIP6 |
| Function | Zinc-influx transporter which plays a role in zinc homeostasis and in the induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (PubMed:12839489, PubMed:18272141, PubMed:21422171, PubMed:23919497, PubMed:27274087, PubMed:34394081). When associated with SLC39A10, the heterodimer formed by SLC39A10 and SLC39A6 mediates cellular zinc uptake to trigger cells to undergo epithelial- to- mesenchymal transition (EMT) (PubMed:27274087). The SLC39A10-SLC39A6 heterodimer also controls NCAM1 phosphorylation and its integration into focal adhesion complexes during EMT (By similarity). Zinc influx inactivates GSK3B, enabling unphosphorylated SNAI1 in the nucleus to down-regulate adherence genes such as CDH1, causing loss of cell adherence (PubMed:23919497). In addition, the SLC39A10-SLC39A6 heterodimer plays an essentiel role in initiating mitosis by importing zinc into cells to initiate a pathway resulting in the onset of mitosis (PubMed:32797246). Participates in the T-cell receptor signaling regulation by mediating cellular zinc uptake into activated lymphocytes (PubMed:21422171, PubMed:30552163, PubMed:34394081). Regulates the zinc influx necessary for proper meiotic progression to metaphase II (MII) that allows the oocyte-to-egg transition (PubMed:25143461). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell projection, lamellipodium membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Membrane raft; Multi-pass membrane protein. Apical cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q4V887} Note=Localizes to lipid rafts in T cells and is recruited into the immunological synapse in response to TCR stimulation (PubMed:34394081) In the choroid plexus is limited to the apical membrane in epithelial cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q4V887, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34394081} |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in the breast, prostate, placenta, kidney, pituitary and corpus callosum (PubMed:12839489). Weakly expressed in heart and intestine. Also highly expressed in cells derived from an adenocarcinoma of the cervix and lung carcinoma (PubMed:12839489). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
ZIP6 Antibody: The zinc transporter ZIP6, also known as SLC39A6, is a member of a family of divalent ion transporters. Zinc is an essential ion for cells and plays significant roles in the growth, development, and differentiation. ZIP6 was initially identified as LIV-1, an estrogen-regulated gene that has been implicated in metastatic breast cancer. Elevated ZIP6 expression has also been reported in human cervical cancer and the HeLa cell line; down-regulation of ZIP6 expression in HeLa by RNAi inhibited cell proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasiveness, as well as decreasing Snail and Slug levels, suggesting ZIP6 plays a regulatory role on the ERK1/2-Snail/Slug pathway.
References
Dufner-Beattie J, Langmade SJ, Wang F, et al. Structure, function, and regulation of a subfamily of mouse zinc transporter genes. J. Biol. Chem.2003; 278:50142-50.
Eide DJ. The SLC39 family of metal ion transporters. Pflugers Arch.2004; 447:796-800.
Taylor KM and Nicohlson RI. The LZT proteins; the LIV-1 subfamily of zinc transporters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta.2003; 1611:16-30.
Taylor KM. LIV-1 breast cancer protein belongs to new family of histidine-rich membrane proteins with potential to control intracellular ZN2+ homeostasis. IUBMB Life2000; 49:249-53.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.