LAMTOR2 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9Y2Q5 |
| Other Accession | NP_054736, 7661728 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
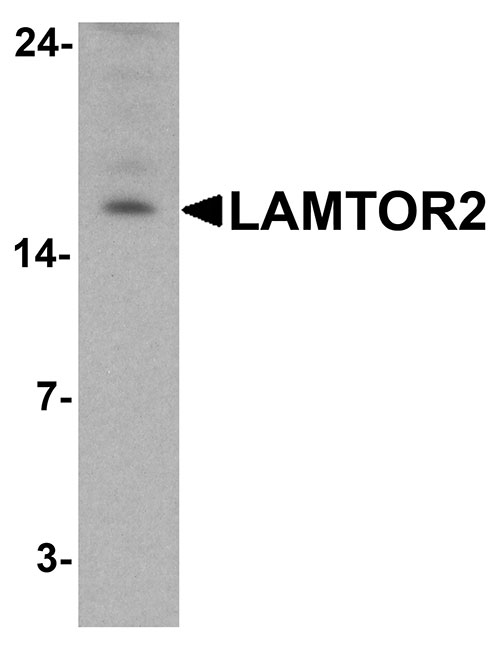
| Calculated MW | Predicted: 14 kDa Observed: 16 kDa |
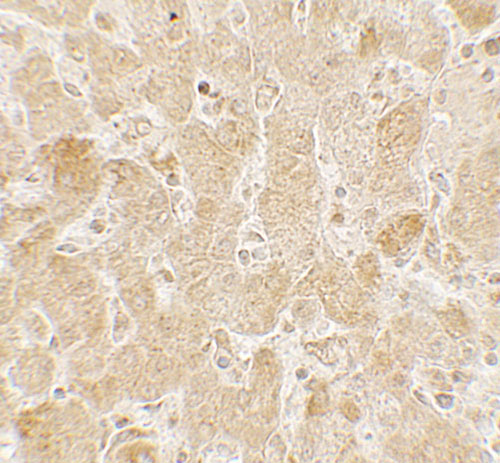
| Application Notes | LAMTOR2 antibody can be used for detection of LAMTOR2 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml. Antibody can also be used for Immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 28956 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | LAMTOR2; LAMTOR2 antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive. At least two isoforms of LAMTOR2 are known to exist; this antibody will detect both isoforms. LAMTOR2 antibody is predicted to not cross-react with other LAMTOR family proteins. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | LAMTOR2 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | LAMTOR2 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | LAMTOR2 (HGNC:29796) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | MAPBPIP, ROBLD3 |
| Function | As part of the Ragulator complex it is involved in amino acid sensing and activation of mTORC1, a signaling complex promoting cell growth in response to growth factors, energy levels, and amino acids (PubMed:20381137, PubMed:28935770, PubMed:29107538, PubMed:29123114, PubMed:29158492). Activated by amino acids through a mechanism involving the lysosomal V-ATPase, the Ragulator plays a dual role for the small GTPases Rag (RagA/RRAGA, RagB/RRAGB, RagC/RRAGC and/or RagD/RRAGD): it (1) acts as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), activating the small GTPases Rag and (2) mediates recruitment of Rag GTPases to the lysosome membrane (PubMed:22980980, PubMed:28935770, PubMed:29107538, PubMed:29123114, PubMed:29158492, PubMed:30181260). Activated Ragulator and Rag GTPases function as a scaffold recruiting mTORC1 to lysosomes where it is in turn activated (PubMed:22980980, PubMed:29107538, PubMed:29123114, PubMed:29158492). Adapter protein that enhances the efficiency of the MAP kinase cascade facilitating the activation of MAPK2 (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Late endosome membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JHS3}; Peripheral membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JHS3}; Cytoplasmic side {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JHS3}. Lysosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JHS3}; Cytoplasmic side {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JHS3}. Note=Recruited to lysosome and endosome membranes by LAMTOR1. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JHS3} |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The late endosomal/lysosomal adaptor MAPK and MTOR activator 2 (LAMTOR2) protein belongs to the LAMTOR family of proteins, and together with LAMTOR3 and the MAPK1 and ERK kinase 1 (MEK1) localizes to late endosomes where it is required for the efficient activation of ERK signaling (1,2). This complex is involved in the regulation of late endosomal traffic and cellular proliferation (3) and plays a role in cellular host defense against Salmonella infection (4).
References
Wunderlich W, Fialka I, Teis D, et al. A novel 14-kilodalton protein interacts with the mitogen-activated protein kinase scaffold MP1 on a late endosomal/lysosomal compartment. J. Cell Biol. 2001; 152:765-76.
Teis D, Wunderlich W, and Huber LA. Localization of the MP1-MAPK scaffold complex to endosomes is mediated by p14 and required for signal transduction. Dev. Cell 2002; 3:803-14.
Teis D, Taub N, Kurzbauer R, et al. p14-MP1-MEK1 signaling regulates endosomal traffic and cellular proliferation during tissue homeostasis. J. Cell Biol. 2006; 175:861-8.
Taub N, Nairz M, Hilber D, et al. The late endosomal adaptor p14 is a macrophage host-defense factor against Salmonella infection. J. Cell Sci. 2012; 125:2698-708.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.