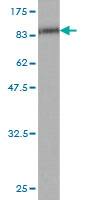
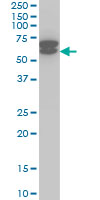
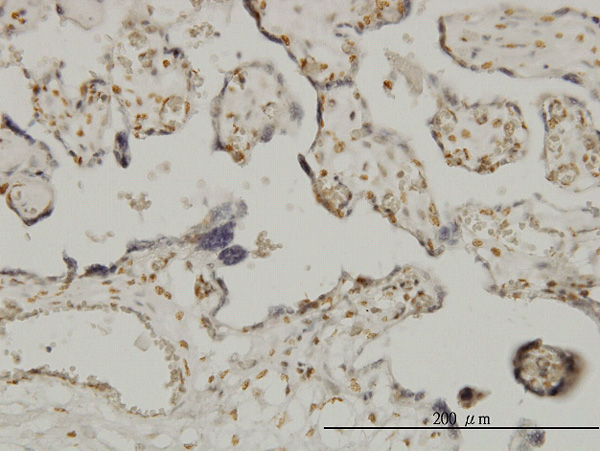
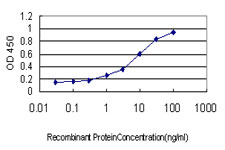
ETV6 Antibody (monoclonal) (M01)
Mouse monoclonal antibody raised against a full length recombinant ETV6.
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P41212 |
| Other Accession | BC043399 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1 Kappa |
| Clone Names | 3B10 |
| Calculated MW | 53000 Da |
| Gene ID | 2120 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Transcription factor ETV6, ETS translocation variant 6, ETS-related protein Tel1, Tel, ETV6, TEL, TEL1 |
| Target/Specificity | ETV6 (AAH43399, 1 a.a. ~ 452 a.a) full-length recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:500~1000 IHC~~1:100~500 E~~N/A |
| Format | Clear, colorless solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2 . |
| Storage | Store at -20°C or lower. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Precautions | ETV6 Antibody (monoclonal) (M01) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This gene encodes an ETS family transcription factor. The product of this gene contains two functional domains: a N-terminal pointed (PNT) domain that is involved in protein-protein interactions with itself and other proteins, and a C-terminal DNA-binding domain. Gene knockout studies in mice suggest that it is required for hematopoiesis and maintenance of the developing vascular network. This gene is known to be involved in a large number of chromosomal rearrangements associated with leukemia and congenital fibrosarcoma.
References
1.ETV6 mutations in early immature human T cell leukemias.Van Vlierberghe P, Ambesi-Impiombato A, Perez-Garcia A, Haydu JE, Rigo I, Hadler M, Tosello V, Della Gatta G, Paietta E, Racevskis J, Wiernik PH, Luger SM, Rowe JM, Rue M, Ferrando AA.J Exp Med. 2011 Dec 19;208(13):2571-9. Epub 2011 Dec 12.2.The ETS Family Member TEL Binds to Nuclear Receptors RAR and RXR and Represses Gene Activation.Meester-Smoor MA, Janssen MJ, Ter Haar WM, van Wely KH, Aarnoudse AJ, van Oord G, van Tilburg GB, Zwarthoff EC.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e23620. Epub 2011 Sep 16.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.