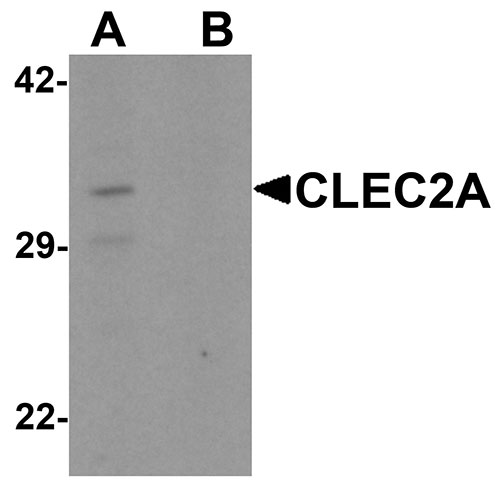
CLEC2A Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q6UVW9 |
| Other Accession | NP_001124183, 195222725 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 19972 Da |
| Application Notes | CLEC2A antibody can be used for detection of CLEC2A by Western blot at 1 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 387836 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | CLEC2A; CLEC2A antibody is human specific. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | CLEC2A antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | CLEC2A Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CLEC2A |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | KACL |
| Function | Membrane-bound protein expressed mainly on keratinocytes which acts as a ligand to stimulate the activating receptor NKp65/KLRF2, expressed on the surface of natural killer (NK) cells (PubMed:25510854). Facilitates thereby dedicated immune recognition of keratinocytes leading to natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity (PubMed:20194751). Also plays a role in modulating the extent of T-cell expansion (PubMed:18550855). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein |
| Tissue Location | Mainly expressed in skin. Also expressed in keratinocytes, spleen, thymus, small intestine, peripheral blood monocytes, bone marrow, ovary, testis and skin. High expression in CD8(+), B-lymphocytes and naive CD4(+) T-cells. Restricted mostly to proliferating lymphocytes. Not detected in myeloid leukocytes or natural killer (NK) cells. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
CLEC2A Antibody: CLEC2A (C-type lectin domain family 2 member A), also known as PILAR (proliferation-induced lymphocyte-associated receptor) is involved in modulating T-cell expansion. It is a 32 kDa single-pass type II membrane protein that contains one C-type lectin domain in its extracellular region and belongs to the CTL/CTLD superfamily. CLEC2A is mainly expressed in skin and highly expressed in CD8(+), B lymphocytes and naive CD4(+) T cells. Manipulation of CLEC2A signaling may be important for treatment of autoimmune diseases and cancer.
References
Huarte E, Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Nesbeth YC, et al. PILAR is a novel modulator of human T-cell expansion. Blood 2008; 112:1259-68.
Drickamer K. C-type lectin-like domains. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1999; 9:585-90
Spreu J, Kienle EC, Schrage B, et al. CLEC2A: a novel, alternatively spliced and skin-associated member of the NKC-encoded AICL-CD69-LLT1 family. Immunogenetics 2007; 59:903-12.
Spreu J, Kuttruff S, Stejfova V, et al. Interaction of C-type lectin-like receptors NKp65 and KACL facilitates dedicated immune recognition of human keratinocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010; 107:5100-5.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.